Indian (Asian) Social Profile
COMPARE
Indian (Asian)
Select to Compare
Social Profile
Indian (Asian) Social Profile
7,850
SOCIAL INDEX
76.0/ 100
SOCIAL RATING
101st/ 347
SOCIAL RANK
Indian (Asian) Geographic Distribution
Indian (Asian) Income
In terms of income, Indians (Asian) residing in the United States exhibit better household income with householder under the age of 25 ($58,239), median female earnings ($46,481), and household income with householder between the ages 25 and 44 ($119,496), but there is room for improvement in wage/income gap percentage (26.4%), household income with householder over the age of 65 ($70,238), and household income with householder between the ages 45 and 64 ($122,343).
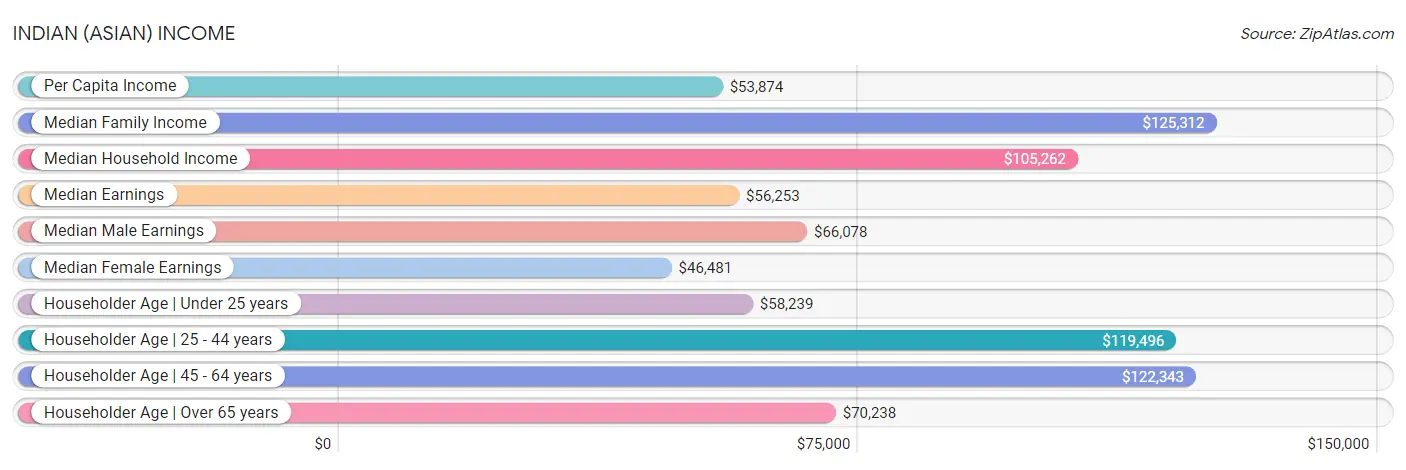
| Income Metric | Rating | Rank | Value |
| Per Capita Income | 100.0 /100 | #22 | Exceptional $53,874 |
| Median Family Income | 100.0 /100 | #17 | Exceptional $125,312 |
| Median Household Income | 100.0 /100 | #12 | Exceptional $105,262 |
| Median Earnings | 100.0 /100 | #15 | Exceptional $56,253 |
| Median Male Earnings | 100.0 /100 | #18 | Exceptional $66,078 |
| Median Female Earnings | 100.0 /100 | #16 | Exceptional $46,481 |
| Householder Age | Under 25 years | 100.0 /100 | #8 | Exceptional $58,239 |
| Householder Age | 25 - 44 years | 100.0 /100 | #10 | Exceptional $119,496 |
| Householder Age | 45 - 64 years | 100.0 /100 | #14 | Exceptional $122,343 |
| Householder Age | Over 65 years | 100.0 /100 | #19 | Exceptional $70,238 |
| Wage/Income Gap | 16.5 /100 | #206 | Poor 26.4% |
Indian (Asian) Poverty
In terms of poverty, Indians (Asian) residing in the United States exhibit better poverty level among single mothers (25.8%), poverty level among single females (17.9%), and poverty level among single males (11.3%), but there is room for improvement in poverty level among seniors over the age of 75 (12.7%), poverty level among seniors over the age of 65 (11.1%), and poverty level among females between the ages 18 and 24 (19.6%).
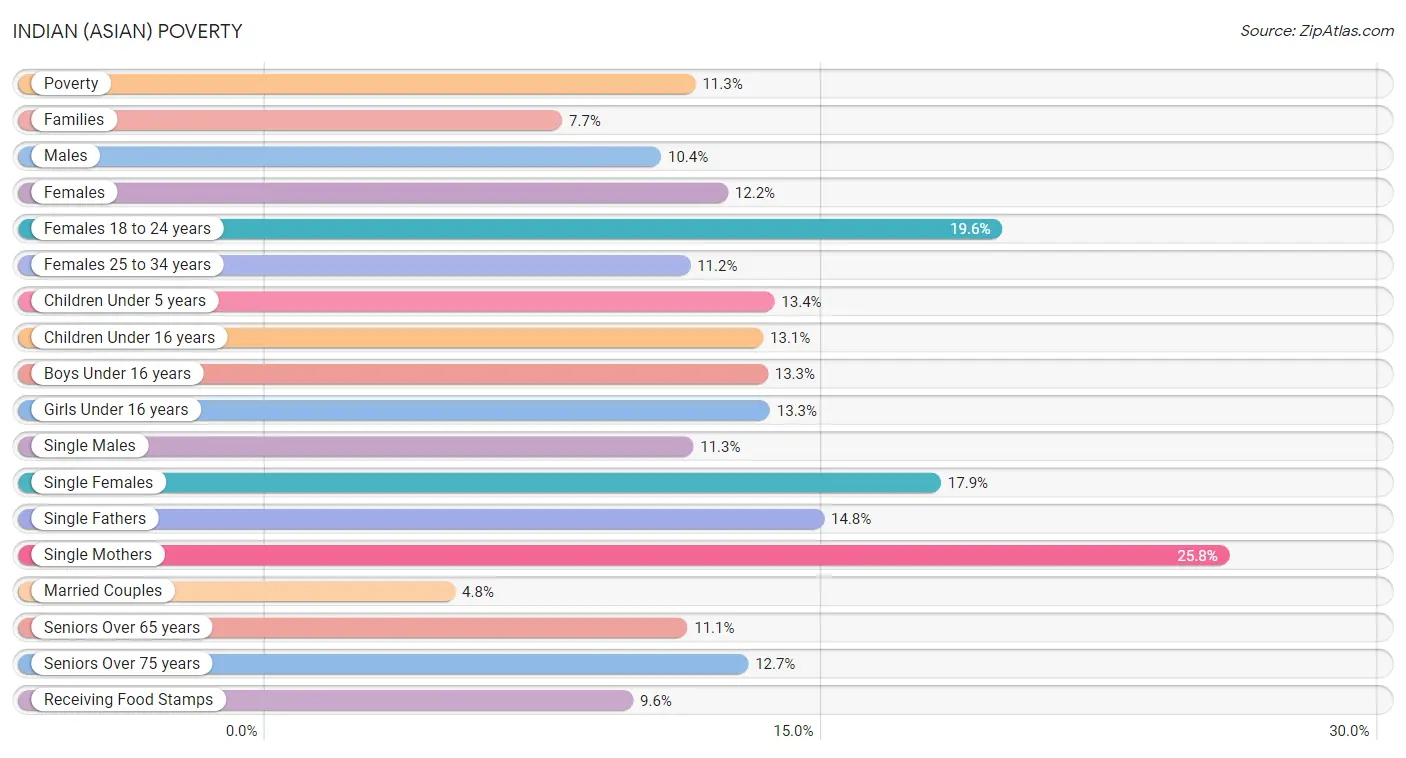
| Poverty Metric | Rating | Rank | Value |
| Poverty | 96.6 /100 | #80 | Exceptional 11.3% |
| Families | 98.8 /100 | #52 | Exceptional 7.7% |
| Males | 94.9 /100 | #90 | Exceptional 10.4% |
| Females | 97.9 /100 | #65 | Exceptional 12.2% |
| Females 18 to 24 years | 88.3 /100 | #139 | Excellent 19.6% |
| Females 25 to 34 years | 100.0 /100 | #14 | Exceptional 11.2% |
| Children Under 5 years | 100.0 /100 | #15 | Exceptional 13.4% |
| Children Under 16 years | 99.8 /100 | #23 | Exceptional 13.1% |
| Boys Under 16 years | 99.9 /100 | #20 | Exceptional 13.3% |
| Girls Under 16 years | 99.9 /100 | #22 | Exceptional 13.3% |
| Single Males | 100.0 /100 | #24 | Exceptional 11.3% |
| Single Females | 100.0 /100 | #15 | Exceptional 17.9% |
| Single Fathers | 100.0 /100 | #41 | Exceptional 14.8% |
| Single Mothers | 100.0 /100 | #13 | Exceptional 25.8% |
| Married Couples | 93.2 /100 | #121 | Exceptional 4.8% |
| Seniors Over 65 years | 34.2 /100 | #190 | Fair 11.1% |
| Seniors Over 75 years | 9.7 /100 | #205 | Tragic 12.7% |
| Receiving Food Stamps | 99.4 /100 | #47 | Exceptional 9.6% |
Indian (Asian) Unemployment
In terms of unemployment, Indians (Asian) residing in the United States exhibit better unemployment rate among women with children between the ages 6 and 17 (7.7%), unemployment rate among women with children under the age of 6 (6.3%), and unemployment rate among seniors over the age of 75 (8.0%), but there is room for improvement in unemployment rate among population between the ages 60 and 64 (5.0%), unemployment rate among population between the ages 55 and 59 (4.9%), and unemployment rate amomg seniors over the age of 65 (5.2%).
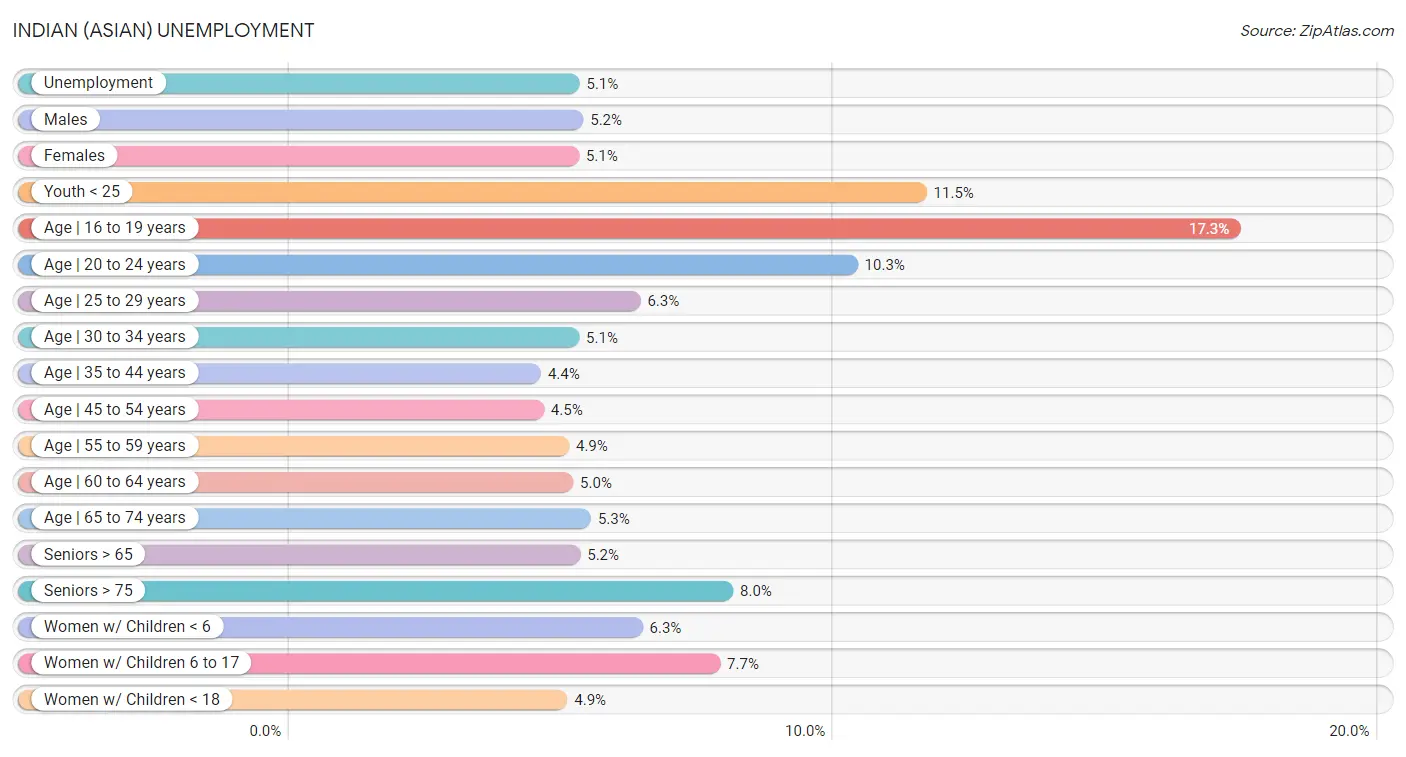
| Unemployment Metric | Rating | Rank | Value |
| Unemployment | 81.6 /100 | #147 | Excellent 5.1% |
| Males | 76.0 /100 | #150 | Good 5.2% |
| Females | 84.2 /100 | #136 | Excellent 5.1% |
| Youth < 25 | 65.1 /100 | #157 | Good 11.5% |
| Age | 16 to 19 years | 77.6 /100 | #145 | Good 17.3% |
| Age | 20 to 24 years | 62.6 /100 | #161 | Good 10.3% |
| Age | 25 to 29 years | 97.8 /100 | #66 | Exceptional 6.3% |
| Age | 30 to 34 years | 97.0 /100 | #61 | Exceptional 5.1% |
| Age | 35 to 44 years | 96.0 /100 | #78 | Exceptional 4.4% |
| Age | 45 to 54 years | 68.1 /100 | #157 | Good 4.5% |
| Age | 55 to 59 years | 7.6 /100 | #220 | Tragic 4.9% |
| Age | 60 to 64 years | 2.2 /100 | #241 | Tragic 5.0% |
| Age | 65 to 74 years | 59.9 /100 | #167 | Average 5.3% |
| Seniors > 65 | 46.6 /100 | #176 | Average 5.2% |
| Seniors > 75 | 99.9 /100 | #69 | Exceptional 8.0% |
| Women w/ Children < 6 | 100.0 /100 | #11 | Exceptional 6.3% |
| Women w/ Children 6 to 17 | 100.0 /100 | #26 | Exceptional 7.7% |
| Women w/ Children < 18 | 99.6 /100 | #22 | Exceptional 4.9% |
Indian (Asian) Labor Participation
In terms of labor participation, Indians (Asian) residing in the United States exhibit better labor force participation rate among population between the ages 30 and 34 (85.4%), labor force participation rate among population between the ages 35 and 44 (84.8%), and labor force participation rate among population between the ages 45 and 54 (83.3%), but there is room for improvement in labor force participation rate among population between the ages 20 and 24 (71.9%), labor force participation rate among population between the ages 16 and 19 (31.9%), and labor force participation rate among population between the ages 25 and 29 (84.7%).
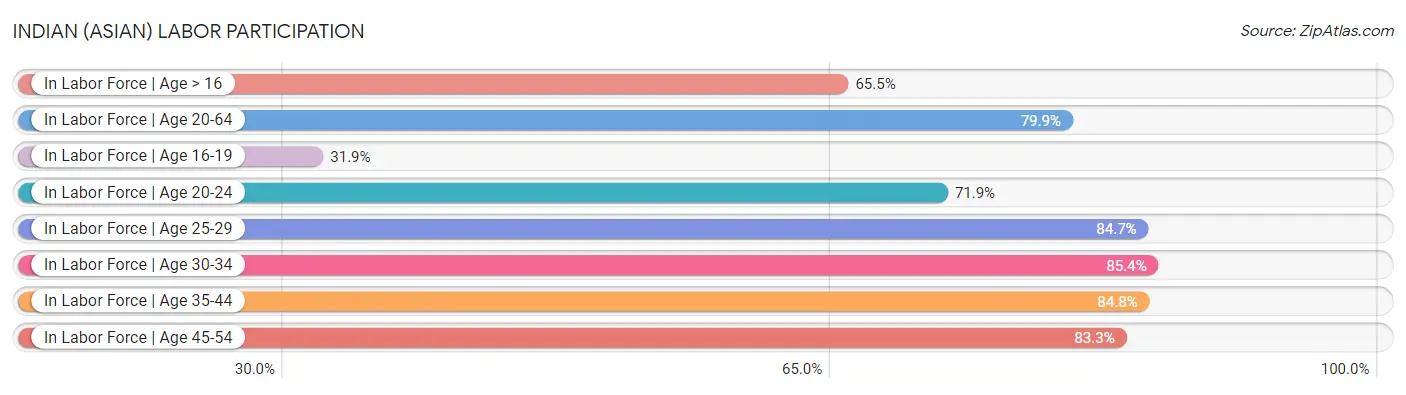
| Labor Participation Metric | Rating | Rank | Value |
| In Labor Force | Age > 16 | 89.5 /100 | #142 | Excellent 65.5% |
| In Labor Force | Age 20-64 | 87.7 /100 | #132 | Excellent 79.9% |
| In Labor Force | Age 16-19 | 0.0 /100 | #311 | Tragic 31.9% |
| In Labor Force | Age 20-24 | 0.0 /100 | #314 | Tragic 71.9% |
| In Labor Force | Age 25-29 | 61.6 /100 | #155 | Good 84.7% |
| In Labor Force | Age 30-34 | 99.0 /100 | #73 | Exceptional 85.4% |
| In Labor Force | Age 35-44 | 96.1 /100 | #98 | Exceptional 84.8% |
| In Labor Force | Age 45-54 | 95.5 /100 | #89 | Exceptional 83.3% |
Indian (Asian) Family Structure
In terms of family structure, Indians (Asian) residing in the United States exhibit better percentage of population currently divorced or separated (10.2%), percentage of single father households (1.9%), and percentage of births to unmarried women (25.3%), but there is room for improvement in percentage of family households with children (27.6%), average family size (3.24), and percentage of population currently married (48.0%).
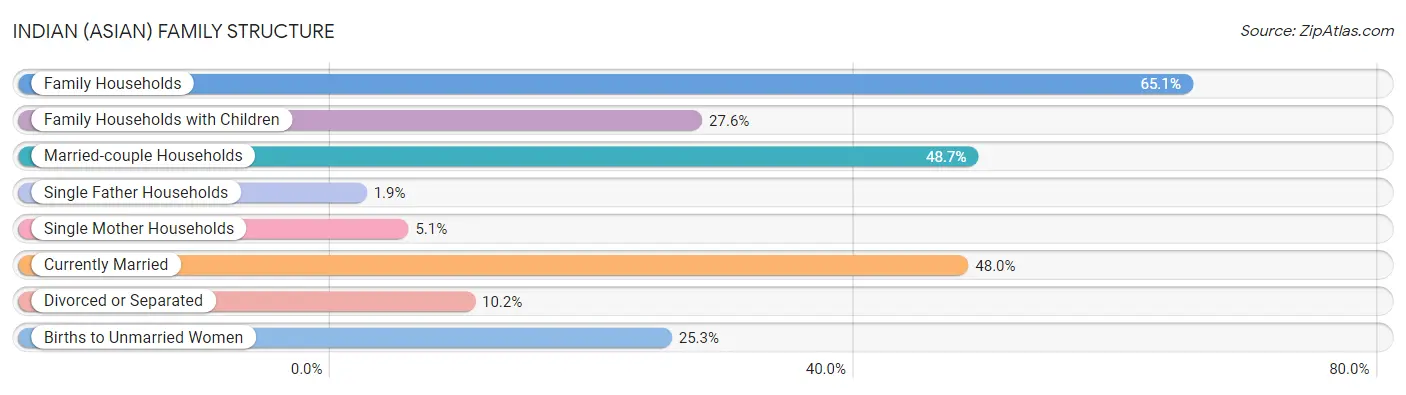
| Family Structure Metric | Rating | Rank | Value |
| Family Households | 97.9 /100 | #103 | Exceptional 65.1% |
| Family Households with Children | 71.6 /100 | #157 | Good 27.6% |
| Married-couple Households | 99.4 /100 | #48 | Exceptional 48.7% |
| Average Family Size | 73.6 /100 | #150 | Good 3.24 |
| Single Father Households | 100.0 /100 | #18 | Exceptional 1.9% |
| Single Mother Households | 99.9 /100 | #16 | Exceptional 5.1% |
| Currently Married | 95.8 /100 | #89 | Exceptional 48.0% |
| Divorced or Separated | 100.0 /100 | #6 | Exceptional 10.2% |
| Births to Unmarried Women | 100.0 /100 | #12 | Exceptional 25.3% |
Indian (Asian) Vehicle Availability
In terms of vehicle availability, Indians (Asian) residing in the United States exhibit better percentage of households with 4 or more vehicles available (6.4%), percentage of households with 3 or more vehicles available (19.1%), and percentage of households with 2 or more vehicles available (53.1%), but there is room for improvement in percentage of households with 1 or more vehicles available (86.0%), percentage of households with no vehicle available (14.1%), and percentage of households with 2 or more vehicles available (53.1%).
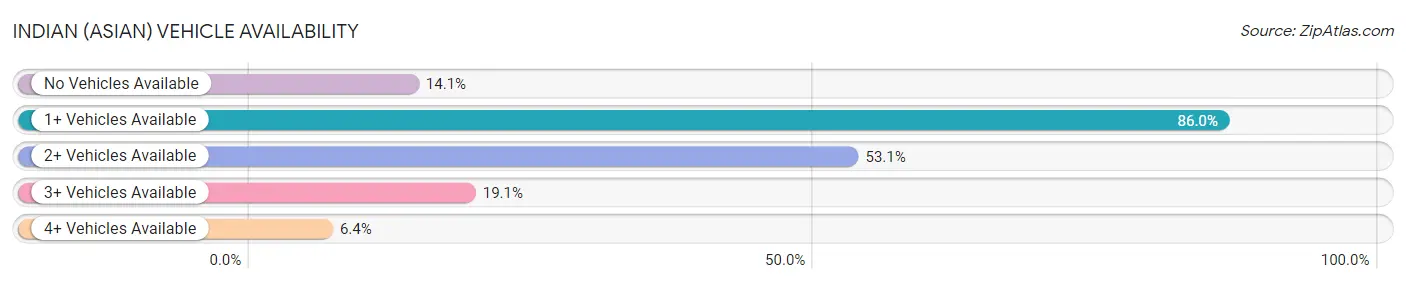
| Vehicle Availability Metric | Rating | Rank | Value |
| No Vehicles Available | 0.0 /100 | #290 | Tragic 14.1% |
| 1+ Vehicles Available | 0.0 /100 | #293 | Tragic 86.0% |
| 2+ Vehicles Available | 1.7 /100 | #244 | Tragic 53.1% |
| 3+ Vehicles Available | 26.0 /100 | #189 | Fair 19.1% |
| 4+ Vehicles Available | 66.3 /100 | #159 | Good 6.4% |
Indian (Asian) Education Level
In terms of education level, Indians (Asian) residing in the United States exhibit better percentage of population with at least doctorate degree education (2.9%), percentage of population with at least professional degree education (6.5%), and percentage of population with at least master's degree education (20.5%), but there is room for improvement in percentage of population with no schooling (2.5%), percentage of population with at least 1st grade education (97.5%), and percentage of population with at least 2nd grade education (97.5%).
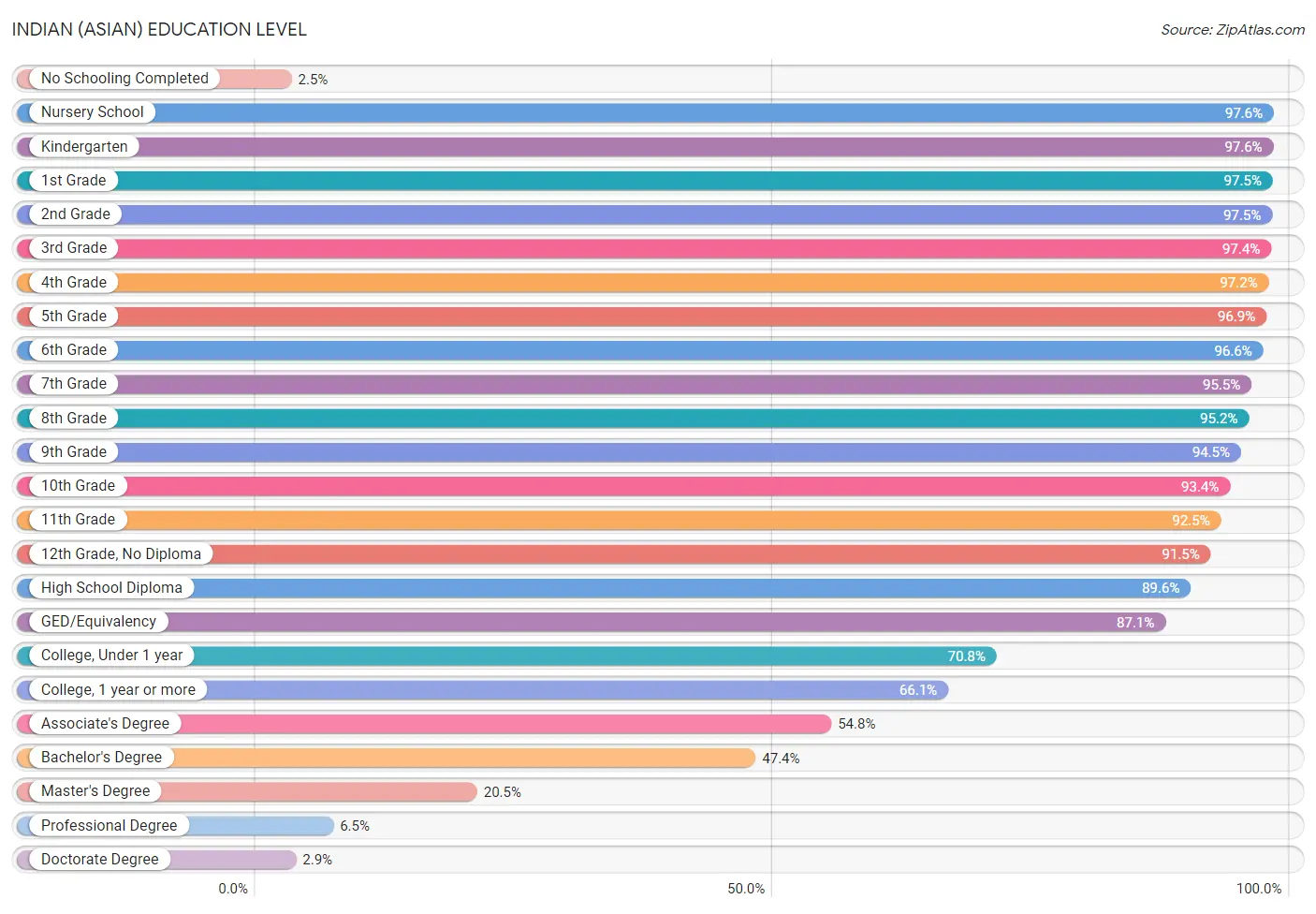
| Education Level Metric | Rating | Rank | Value |
| No Schooling Completed | 0.4 /100 | #264 | Tragic 2.5% |
| Nursery School | 0.9 /100 | #248 | Tragic 97.6% |
| Kindergarten | 1.0 /100 | #246 | Tragic 97.6% |
| 1st Grade | 0.6 /100 | #258 | Tragic 97.5% |
| 2nd Grade | 0.6 /100 | #254 | Tragic 97.5% |
| 3rd Grade | 1.3 /100 | #243 | Tragic 97.4% |
| 4th Grade | 1.9 /100 | #238 | Tragic 97.2% |
| 5th Grade | 1.9 /100 | #240 | Tragic 96.9% |
| 6th Grade | 1.9 /100 | #239 | Tragic 96.6% |
| 7th Grade | 2.3 /100 | #238 | Tragic 95.5% |
| 8th Grade | 3.3 /100 | #232 | Tragic 95.2% |
| 9th Grade | 8.6 /100 | #220 | Tragic 94.5% |
| 10th Grade | 17.6 /100 | #210 | Poor 93.4% |
| 11th Grade | 51.5 /100 | #173 | Average 92.5% |
| 12th Grade, No Diploma | 79.4 /100 | #148 | Good 91.5% |
| High School Diploma | 78.8 /100 | #142 | Good 89.6% |
| GED/Equivalency | 95.9 /100 | #105 | Exceptional 87.1% |
| College, Under 1 year | 99.9 /100 | #31 | Exceptional 70.8% |
| College, 1 year or more | 100.0 /100 | #25 | Exceptional 66.1% |
| Associate's Degree | 100.0 /100 | #18 | Exceptional 54.8% |
| Bachelor's Degree | 100.0 /100 | #18 | Exceptional 47.4% |
| Master's Degree | 100.0 /100 | #20 | Exceptional 20.5% |
| Professional Degree | 100.0 /100 | #19 | Exceptional 6.5% |
| Doctorate Degree | 100.0 /100 | #11 | Exceptional 2.9% |
Indian (Asian) Disability
In terms of disability, Indians (Asian) residing in the United States exhibit better percentage of population with a disability between the ages 5 and 17 (4.6%), percentage of females with a disability (10.8%), and percentage of population with a disability (10.3%), but there is room for improvement in percentage of population with a disability over the age of 75 (46.5%), percentage of population with cognitive disability (16.8%), and percentage of population with hearing disability (2.7%).
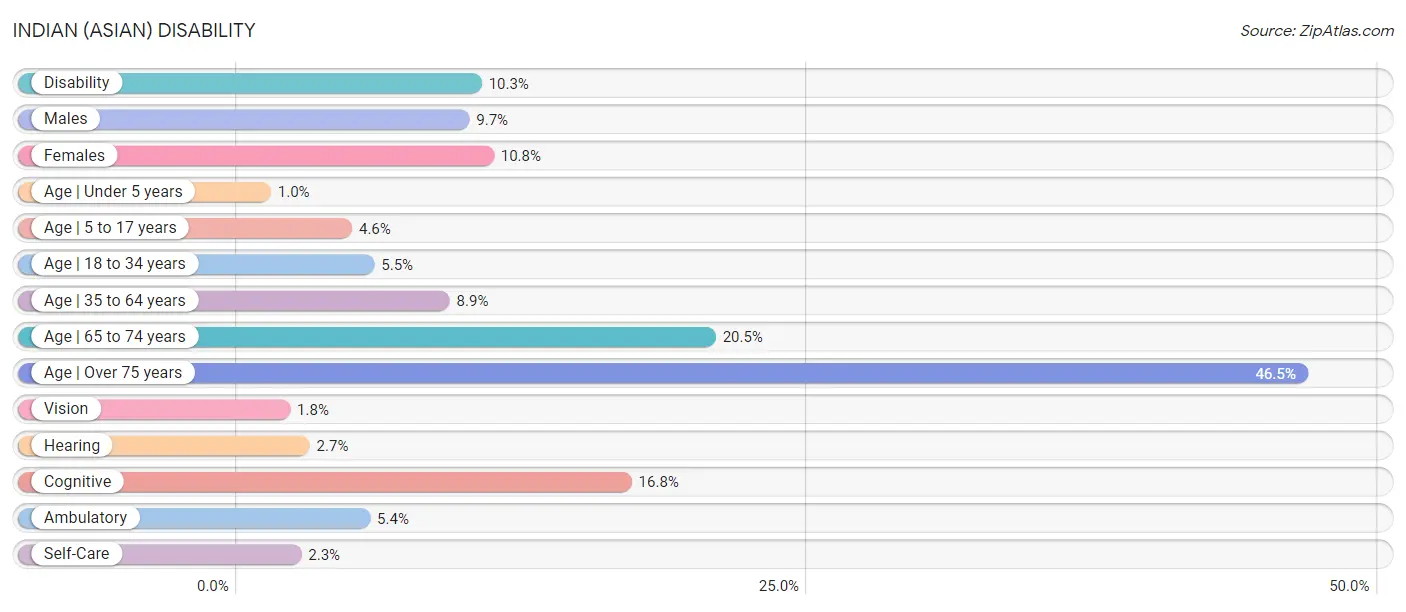
| Disability Metric | Rating | Rank | Value |
| Disability | 100.0 /100 | #16 | Exceptional 10.3% |
| Males | 100.0 /100 | #15 | Exceptional 9.7% |
| Females | 100.0 /100 | #17 | Exceptional 10.8% |
| Age | Under 5 years | 100.0 /100 | #24 | Exceptional 1.0% |
| Age | 5 to 17 years | 100.0 /100 | #8 | Exceptional 4.6% |
| Age | 18 to 34 years | 100.0 /100 | #14 | Exceptional 5.5% |
| Age | 35 to 64 years | 100.0 /100 | #12 | Exceptional 8.9% |
| Age | 65 to 74 years | 100.0 /100 | #14 | Exceptional 20.5% |
| Age | Over 75 years | 95.7 /100 | #116 | Exceptional 46.5% |
| Vision | 100.0 /100 | #16 | Exceptional 1.8% |
| Hearing | 98.4 /100 | #63 | Exceptional 2.7% |
| Cognitive | 97.2 /100 | #112 | Exceptional 16.8% |
| Ambulatory | 100.0 /100 | #19 | Exceptional 5.4% |
| Self-Care | 98.7 /100 | #83 | Exceptional 2.3% |
Common Questions
What are the strongest characteristics of Indians (Asian) in the United States?
The strongest characteristics of Indians (Asian) in the United States are:
#1
Percentage of Population Currently Divorced or Separated
10.2%
(100.0/100)
#2
Percentage of Population with at least Doctorate Degree Education
2.9%
(100.0/100)
#3
Percentage of Population with a Disability Between the Ages 5 and 17
4.6%
(100.0/100)
#4
Household Income with Householder Under the Age of 25
$58,239
(100.0/100)
#5
Median Female Earnings
$46,481
(100.0/100)
What are the most vital challenges facing Indians (Asian) in the United States?
The most vital challenges facing Indians (Asian) in the United States are:
#1
Labor Force Participation Rate Among Population Between the Ages 20 and 24
71.9%
(0.0/100)
#2
Percentage of Households with 1 or More Vehicles Available
86.0%
(0.0/100)
#3
Percentage of Households with No Vehicle Available
14.1%
(0.0/100)
#4
Labor Force Participation Rate Among Population Between the Ages 16 and 19
31.9%
(0.0/100)
#5
Percentage of Population with No Schooling
2.5%
(0.4/100)
What is Indian (Asian) per capita income in the United States?
Indian (Asian) per capita income in the United States is $53,874, which is exceptional, ranking it 22nd out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) median family income in the United States?
Indian (Asian) median family income in the United States is $125,312, which is exceptional, ranking it 17th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) median household income in the United States?
Indian (Asian) median household income in the United States is $105,262, which is exceptional, ranking it 12th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) median earnings in the United States?
Indian (Asian) median earnings in the United States is $56,253, which is exceptional, ranking it 15th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) median male earnings in the United States?
Indian (Asian) median male earnings in the United States is $66,078, which is exceptional, ranking it 18th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) median female earnings in the United States?
Indian (Asian) median female earnings in the United States is $46,481, which is exceptional, ranking it 16th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) wage/income gap percentage in the United States?
Indian (Asian) wage/income gap percentage in the United States is 26.4%, which is poor, ranking it 206th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) poverty level in the United States?
Indian (Asian) poverty level in the United States is 11.3%, which is exceptional, ranking it 80th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) poverty level among families in the United States?
Indian (Asian) poverty level among families in the United States is 7.7%, which is exceptional, ranking it 52nd out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) poverty level among males in the United States?
Indian (Asian) poverty level among males in the United States is 10.4%, which is exceptional, ranking it 90th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) poverty level among females in the United States?
Indian (Asian) poverty level among females in the United States is 12.2%, which is exceptional, ranking it 65th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) poverty level among children under the age of 16 in the United States?
Indian (Asian) poverty level among children under the age of 16 in the United States is 13.1%, which is exceptional, ranking it 23rd out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) poverty level among single males in the United States?
Indian (Asian) poverty level among single males in the United States is 11.3%, which is exceptional, ranking it 24th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) poverty level among single females in the United States?
Indian (Asian) poverty level among single females in the United States is 17.9%, which is exceptional, ranking it 15th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) poverty level among single fathers in the United States?
Indian (Asian) poverty level among single fathers in the United States is 14.8%, which is exceptional, ranking it 41st out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) poverty level among single mothers in the United States?
Indian (Asian) poverty level among single mothers in the United States is 25.8%, which is exceptional, ranking it 13th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) percentage of population receiving government assistance and/or food stamps in the United States?
Indian (Asian) percentage of population receiving government assistance and/or food stamps in the United States is 9.6%, which is exceptional, ranking it 47th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) unemployment in the United States?
Indian (Asian) unemployment in the United States is 5.1%, which is excellent, ranking it 147th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) unemployment rate among males in the United States?
Indian (Asian) unemployment rate among males in the United States is 5.2%, which is good, ranking it 150th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) unemploymnet rate among females in the United States?
Indian (Asian) unemploymnet rate among females in the United States is 5.1%, which is excellent, ranking it 136th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) percentage of family households in the United States?
Indian (Asian) percentage of family households in the United States is 65.1%, which is exceptional, ranking it 103rd out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) percentage of family households with children in the United States?
Indian (Asian) percentage of family households with children in the United States is 27.6%, which is good, ranking it 157th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) percentage of married-couple family households in the United States?
Indian (Asian) percentage of married-couple family households in the United States is 48.7%, which is exceptional, ranking it 48th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) average family size in the United States?
Indian (Asian) average family size in the United States is 3.24, which is good, ranking it 150th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) percentage of single father households in the United States?
Indian (Asian) percentage of single father households in the United States is 1.9%, which is exceptional, ranking it 18th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) percentage of single mother households in the United States?
Indian (Asian) percentage of single mother households in the United States is 5.1%, which is exceptional, ranking it 16th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) percentage of population currently married in the United States?
Indian (Asian) percentage of population currently married in the United States is 48.0%, which is exceptional, ranking it 89th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) percentage of population currently divorced or separated in the United States?
Indian (Asian) percentage of population currently divorced or separated in the United States is 10.2%, which is exceptional, ranking it 6th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) percentage of births to unmarried women in the United States?
Indian (Asian) percentage of births to unmarried women in the United States is 25.3%, which is exceptional, ranking it 12th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) percentage of population with a disability in the United States?
Indian (Asian) percentage of population with a disability in the United States is 10.3%, which is exceptional, ranking it 16th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) percentage of males with a disability in the United States?
Indian (Asian) percentage of males with a disability in the United States is 9.7%, which is exceptional, ranking it 15th out of 347 demographic groups.
What is Indian (Asian) percentage of females with a disability in the United States?
Indian (Asian) percentage of females with a disability in the United States is 10.8%, which is exceptional, ranking it 17th out of 347 demographic groups.
Definitions
Social Index (Si) is a quantitative measure of societal well-being and progress based on various factors and indicators.
Social Index Explained
Social Index refers to a cumulative metric used to assess and measure the overall well-being or social standing of a specific demographic group within a society. It combines multiple factors such as income, poverty rates, family structure, education levels, employment and unemployment rates, rates of illegitimate childbirths, divorce rates, and other relevant social indicators. The purpose of a social index is to provide a comprehensive snapshot of the social conditions and quality of life within a particular group.
Social Index Calculation
The calculation of a social index involves assigning weights or scores to various social factors and then summing up these scores to obtain an overall composite score. These scores are then multiplied by their respective weights and summed up to calculate the overall social index score for the demographic group being assessed. The resulting score provides a quantitative measure of the group's social well-being, allowing for comparisons, tracking changes over time, and informing policy and decision-making processes.
What Can Social Index be Used For
A social index can be used for various purposes, including:
- Assessing Social Well-being: The social index provides a quantitative measure of the overall well-being of a demographic group. It helps assess the social conditions, quality of life, and disparities within a population, allowing policymakers, researchers, and organizations to identify areas that require improvement or targeted interventions.
- Policy Evaluation: The index can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of social policies and interventions. By tracking changes in the social index score over time, policymakers can assess the impact of specific initiatives and make data-driven decisions regarding resource allocation and policy adjustments.
- Targeting Resources: The social index helps identify demographic groups or geographic regions that are facing greater social challenges or experiencing lower levels of well-being. It assists in targeting resources and interventions to address specific social issues, reduce disparities, and promote equitable development.
- Comparing Demographic Groups: The social index allows for comparisons between different demographic groups or across different regions. It provides insights into the relative social standing or well-being of these groups, facilitating a deeper understanding of disparities and informing policy efforts to address them.
- Advocacy and Awareness: The social index can be used as a tool for advocacy and raising awareness about social issues. By quantifying and visualizing social conditions, the index helps highlight areas of concern, draw attention to inequalities, and mobilize support for social change and policy reforms.
- Monitoring Progress: The index serves as a benchmark for monitoring progress and evaluating the impact of social development initiatives. It enables stakeholders to track changes in social indicators, identify trends, and measure the effectiveness of interventions over time.
- Academic and Research Purposes: The social index provides researchers with a comprehensive metric to study social phenomena and investigate the relationship between different social factors. It helps generate insights, support academic research, and contribute to the body of knowledge on social well-being and development.
- Overall, the social index serves as a valuable tool for understanding, measuring, and addressing social challenges. It informs policy decisions, facilitates targeted interventions, and promotes a more holistic approach to social development and well-being.