Indonesian vs Ute Community Comparison
COMPARE
Indonesian
Ute
Social Comparison
Social Comparison
Indonesians
Ute
2,685
SOCIAL INDEX
24.4/ 100
SOCIAL RATING
247th/ 347
SOCIAL RANK
2,439
SOCIAL INDEX
21.9/ 100
SOCIAL RATING
258th/ 347
SOCIAL RANK
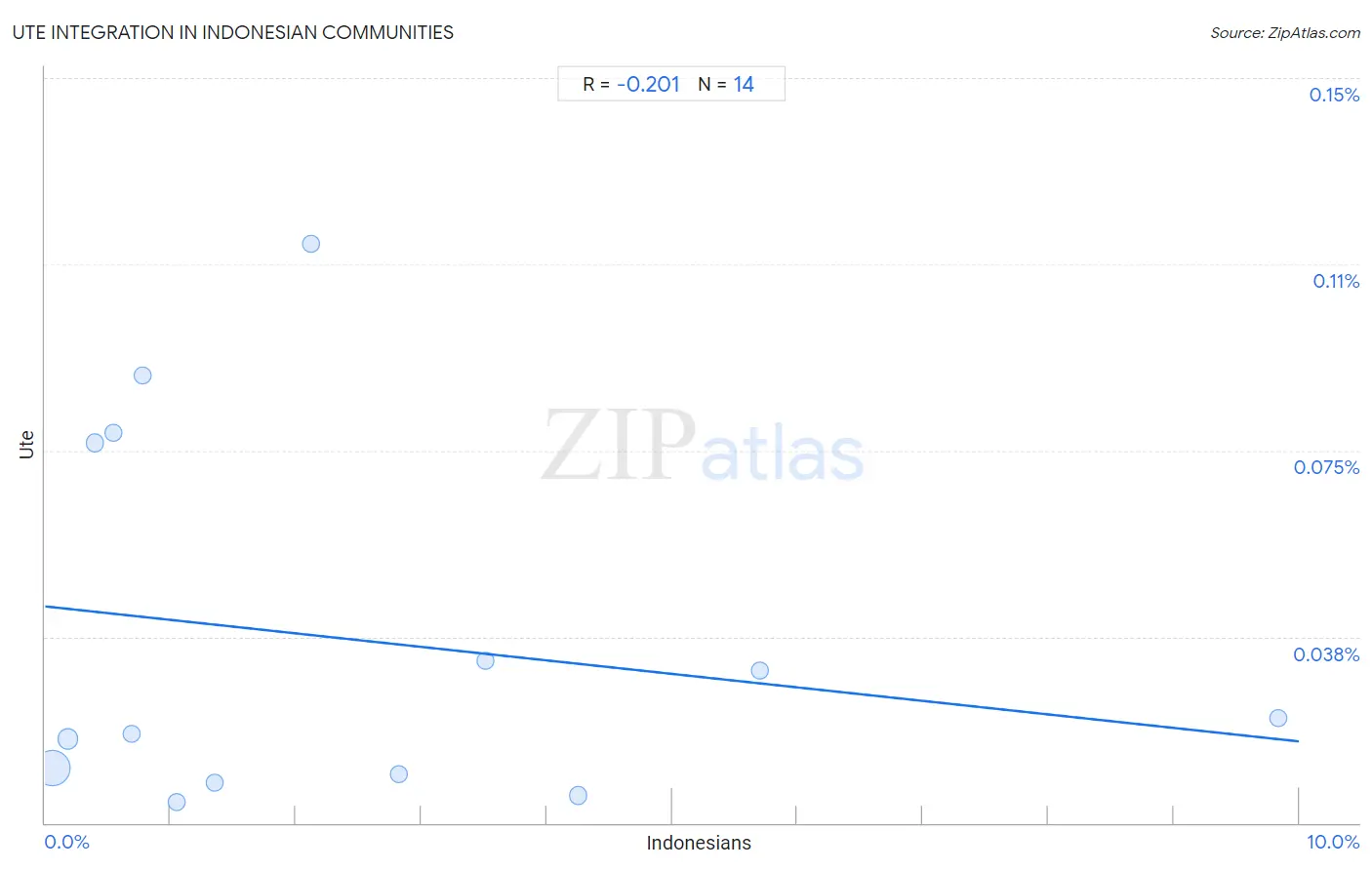
Ute Integration in Indonesian Communities
The statistical analysis conducted on geographies consisting of 39,377,694 people shows a weak negative correlation between the proportion of Ute within Indonesian communities in the United States with a correlation coefficient (R) of -0.201. On average, for every 1% (one percent) increase in Indonesians within a typical geography, there is a decrease of 0.003% in Ute. To illustrate, in a geography comprising of 100,000 individuals, a rise of 1,000 Indonesians corresponds to a decrease of 2.7 Ute.
Indonesian vs Ute Income
When considering income, the most significant differences between Indonesian and Ute communities in the United States are seen in wage/income gap (22.7% compared to 27.8%, a difference of 22.3%), householder income under 25 years ($45,566 compared to $49,997, a difference of 9.7%), and median female earnings ($36,140 compared to $34,960, a difference of 3.4%). Conversely, both communities are more comparable in terms of median household income ($72,856 compared to $72,402, a difference of 0.63%), median family income ($88,301 compared to $87,596, a difference of 0.80%), and householder income ages 45 - 64 years ($84,890 compared to $83,937, a difference of 1.1%).

| Income Metric | Indonesian | Ute |
| Per Capita Income | Tragic $37,300 | Tragic $36,651 |
| Median Family Income | Tragic $88,301 | Tragic $87,596 |
| Median Household Income | Tragic $72,856 | Tragic $72,402 |
| Median Earnings | Tragic $41,701 | Tragic $41,051 |
| Median Male Earnings | Tragic $47,503 | Tragic $48,899 |
| Median Female Earnings | Tragic $36,140 | Tragic $34,960 |
| Householder Age | Under 25 years | Tragic $45,566 | Tragic $49,997 |
| Householder Age | 25 - 44 years | Tragic $79,543 | Tragic $82,166 |
| Householder Age | 45 - 64 years | Tragic $84,890 | Tragic $83,937 |
| Householder Age | Over 65 years | Tragic $54,176 | Tragic $52,949 |
| Wage/Income Gap | Exceptional 22.7% | Tragic 27.8% |
Indonesian vs Ute Poverty
When considering poverty, the most significant differences between Indonesian and Ute communities in the United States are seen in male poverty (13.8% compared to 16.2%, a difference of 17.3%), single female poverty (24.3% compared to 28.4%, a difference of 17.1%), and female poverty among 18-24 year olds (22.5% compared to 25.4%, a difference of 13.0%). Conversely, both communities are more comparable in terms of married-couple family poverty (6.3% compared to 6.4%, a difference of 1.7%), child poverty among girls under 16 (21.3% compared to 21.8%, a difference of 2.5%), and child poverty under the age of 16 (21.0% compared to 21.5%, a difference of 2.7%).
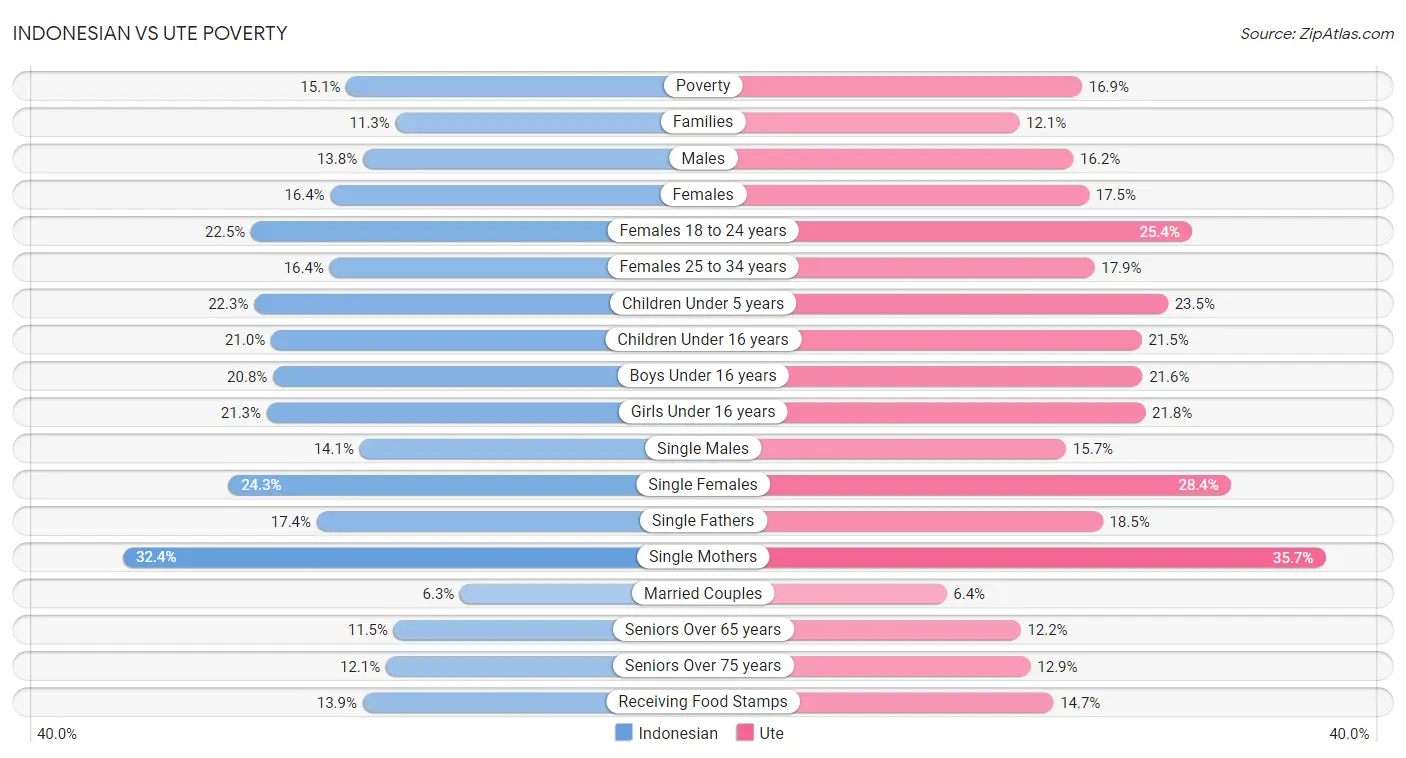
| Poverty Metric | Indonesian | Ute |
| Poverty | Tragic 15.1% | Tragic 16.9% |
| Families | Tragic 11.3% | Tragic 12.1% |
| Males | Tragic 13.8% | Tragic 16.2% |
| Females | Tragic 16.4% | Tragic 17.5% |
| Females 18 to 24 years | Tragic 22.5% | Tragic 25.4% |
| Females 25 to 34 years | Tragic 16.4% | Tragic 17.9% |
| Children Under 5 years | Tragic 22.3% | Tragic 23.5% |
| Children Under 16 years | Tragic 21.0% | Tragic 21.5% |
| Boys Under 16 years | Tragic 20.8% | Tragic 21.6% |
| Girls Under 16 years | Tragic 21.3% | Tragic 21.8% |
| Single Males | Tragic 14.1% | Tragic 15.7% |
| Single Females | Tragic 24.3% | Tragic 28.4% |
| Single Fathers | Tragic 17.4% | Tragic 18.5% |
| Single Mothers | Tragic 32.4% | Tragic 35.7% |
| Married Couples | Tragic 6.3% | Tragic 6.4% |
| Seniors Over 65 years | Poor 11.5% | Tragic 12.2% |
| Seniors Over 75 years | Good 12.1% | Tragic 12.9% |
| Receiving Food Stamps | Tragic 13.9% | Tragic 14.7% |
Indonesian vs Ute Unemployment
When considering unemployment, the most significant differences between Indonesian and Ute communities in the United States are seen in unemployment among ages 45 to 54 years (4.4% compared to 6.2%, a difference of 41.9%), unemployment among seniors over 65 years (4.5% compared to 6.3%, a difference of 39.3%), and unemployment among ages 65 to 74 years (4.7% compared to 6.5%, a difference of 39.1%). Conversely, both communities are more comparable in terms of unemployment among women with children ages 6 to 17 years (7.4% compared to 7.0%, a difference of 5.7%), unemployment among women with children under 18 years (5.5% compared to 5.9%, a difference of 7.6%), and unemployment among ages 25 to 29 years (6.1% compared to 6.8%, a difference of 11.5%).

| Unemployment Metric | Indonesian | Ute |
| Unemployment | Excellent 5.1% | Tragic 6.3% |
| Males | Good 5.2% | Tragic 6.6% |
| Females | Exceptional 5.0% | Tragic 6.1% |
| Youth < 25 | Exceptional 10.6% | Tragic 13.3% |
| Age | 16 to 19 years | Exceptional 15.5% | Tragic 19.6% |
| Age | 20 to 24 years | Exceptional 9.0% | Tragic 11.2% |
| Age | 25 to 29 years | Exceptional 6.1% | Poor 6.8% |
| Age | 30 to 34 years | Exceptional 5.2% | Tragic 7.0% |
| Age | 35 to 44 years | Average 4.7% | Tragic 5.3% |
| Age | 45 to 54 years | Exceptional 4.4% | Tragic 6.2% |
| Age | 55 to 59 years | Exceptional 4.3% | Tragic 5.2% |
| Age | 60 to 64 years | Exceptional 4.2% | Fair 4.9% |
| Age | 65 to 74 years | Exceptional 4.7% | Tragic 6.5% |
| Seniors > 65 | Exceptional 4.5% | Tragic 6.3% |
| Seniors > 75 | Exceptional 7.9% | Exceptional 6.8% |
| Women w/ Children < 6 | Average 7.7% | Exceptional 6.5% |
| Women w/ Children 6 to 17 | Exceptional 7.4% | Exceptional 7.0% |
| Women w/ Children < 18 | Fair 5.5% | Tragic 5.9% |
Indonesian vs Ute Labor Participation
When considering labor participation, the most significant differences between Indonesian and Ute communities in the United States are seen in in labor force | age 16-19 (40.7% compared to 37.1%, a difference of 9.8%), in labor force | age > 16 (66.3% compared to 60.9%, a difference of 8.9%), and in labor force | age 20-64 (79.4% compared to 73.7%, a difference of 7.8%). Conversely, both communities are more comparable in terms of in labor force | age 20-24 (77.2% compared to 73.8%, a difference of 4.6%), in labor force | age 25-29 (84.7% compared to 80.8%, a difference of 4.8%), and in labor force | age 35-44 (83.7% compared to 79.4%, a difference of 5.4%).
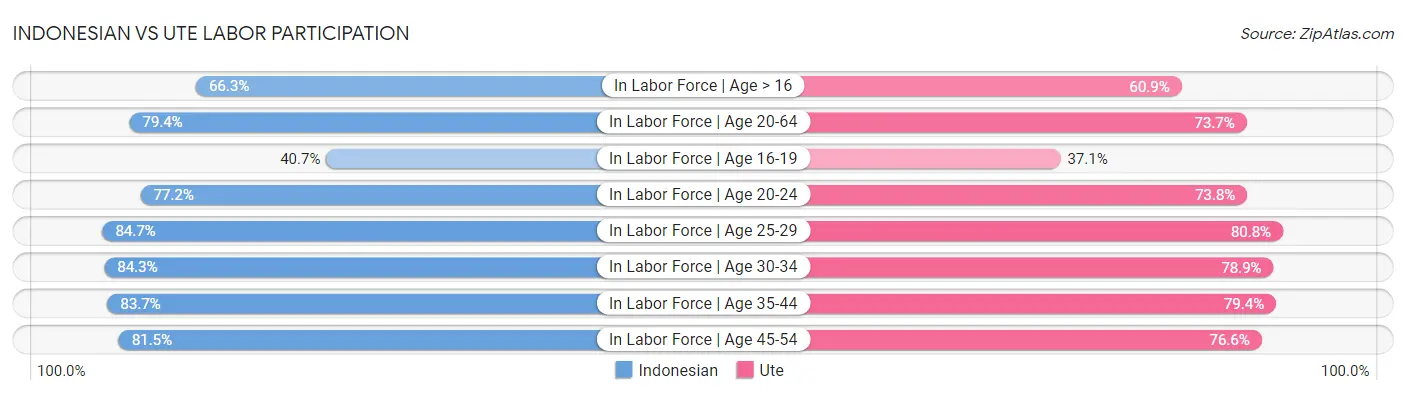
| Labor Participation Metric | Indonesian | Ute |
| In Labor Force | Age > 16 | Exceptional 66.3% | Tragic 60.9% |
| In Labor Force | Age 20-64 | Fair 79.4% | Tragic 73.7% |
| In Labor Force | Age 16-19 | Exceptional 40.7% | Good 37.1% |
| In Labor Force | Age 20-24 | Exceptional 77.2% | Tragic 73.8% |
| In Labor Force | Age 25-29 | Average 84.7% | Tragic 80.8% |
| In Labor Force | Age 30-34 | Tragic 84.3% | Tragic 78.9% |
| In Labor Force | Age 35-44 | Tragic 83.7% | Tragic 79.4% |
| In Labor Force | Age 45-54 | Tragic 81.5% | Tragic 76.6% |
Indonesian vs Ute Family Structure
When considering family structure, the most significant differences between Indonesian and Ute communities in the United States are seen in single father households (2.6% compared to 3.0%, a difference of 15.5%), average family size (3.28 compared to 3.49, a difference of 6.5%), and births to unmarried women (35.0% compared to 33.0%, a difference of 6.0%). Conversely, both communities are more comparable in terms of family households with children (28.1% compared to 28.2%, a difference of 0.12%), divorced or separated (12.6% compared to 12.6%, a difference of 0.40%), and currently married (43.5% compared to 43.9%, a difference of 0.95%).
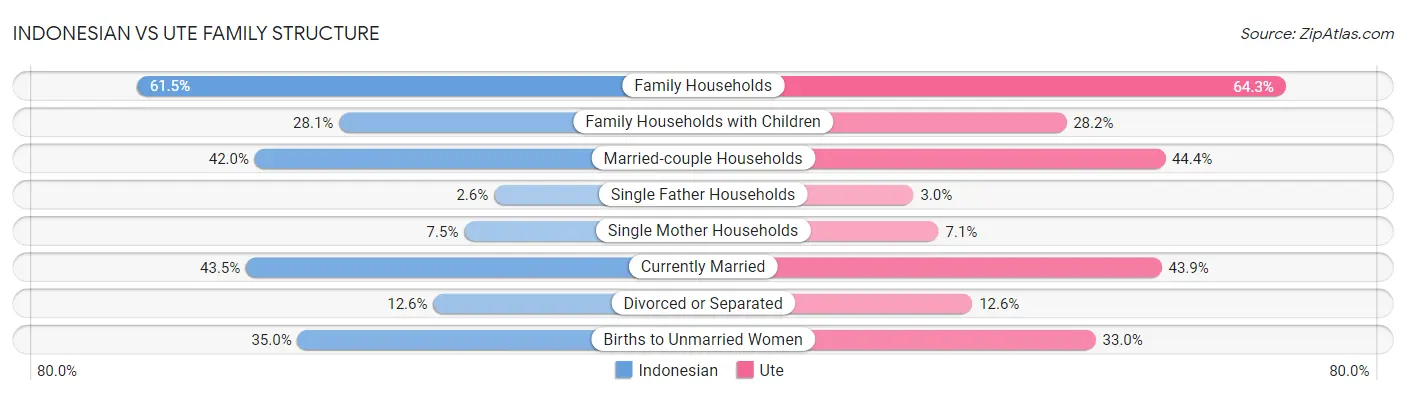
| Family Structure Metric | Indonesian | Ute |
| Family Households | Tragic 61.5% | Average 64.3% |
| Family Households with Children | Exceptional 28.1% | Exceptional 28.2% |
| Married-couple Households | Tragic 42.0% | Tragic 44.4% |
| Average Family Size | Exceptional 3.28 | Exceptional 3.49 |
| Single Father Households | Tragic 2.6% | Tragic 3.0% |
| Single Mother Households | Tragic 7.5% | Tragic 7.1% |
| Currently Married | Tragic 43.5% | Tragic 43.9% |
| Divorced or Separated | Tragic 12.6% | Tragic 12.6% |
| Births to Unmarried Women | Tragic 35.0% | Poor 33.0% |
Indonesian vs Ute Vehicle Availability
When considering vehicle availability, the most significant differences between Indonesian and Ute communities in the United States are seen in 4 or more vehicles in household (6.0% compared to 8.8%, a difference of 47.0%), 3 or more vehicles in household (18.3% compared to 22.7%, a difference of 24.0%), and no vehicles in household (10.3% compared to 11.6%, a difference of 12.5%). Conversely, both communities are more comparable in terms of 1 or more vehicles in household (89.7% compared to 88.7%, a difference of 1.2%), 2 or more vehicles in household (53.4% compared to 56.6%, a difference of 6.0%), and no vehicles in household (10.3% compared to 11.6%, a difference of 12.5%).

| Vehicle Availability Metric | Indonesian | Ute |
| No Vehicles Available | Average 10.3% | Tragic 11.6% |
| 1+ Vehicles Available | Average 89.7% | Tragic 88.7% |
| 2+ Vehicles Available | Tragic 53.4% | Exceptional 56.6% |
| 3+ Vehicles Available | Tragic 18.3% | Exceptional 22.7% |
| 4+ Vehicles Available | Tragic 6.0% | Exceptional 8.8% |
Indonesian vs Ute Education Level
When considering education level, the most significant differences between Indonesian and Ute communities in the United States are seen in no schooling completed (3.2% compared to 2.3%, a difference of 42.0%), doctorate degree (1.6% compared to 2.0%, a difference of 25.9%), and professional degree (3.7% compared to 4.0%, a difference of 9.5%). Conversely, both communities are more comparable in terms of high school diploma (86.5% compared to 86.2%, a difference of 0.40%), 12th grade, no diploma (88.6% compared to 89.0%, a difference of 0.45%), and 11th grade (90.3% compared to 91.1%, a difference of 0.86%).
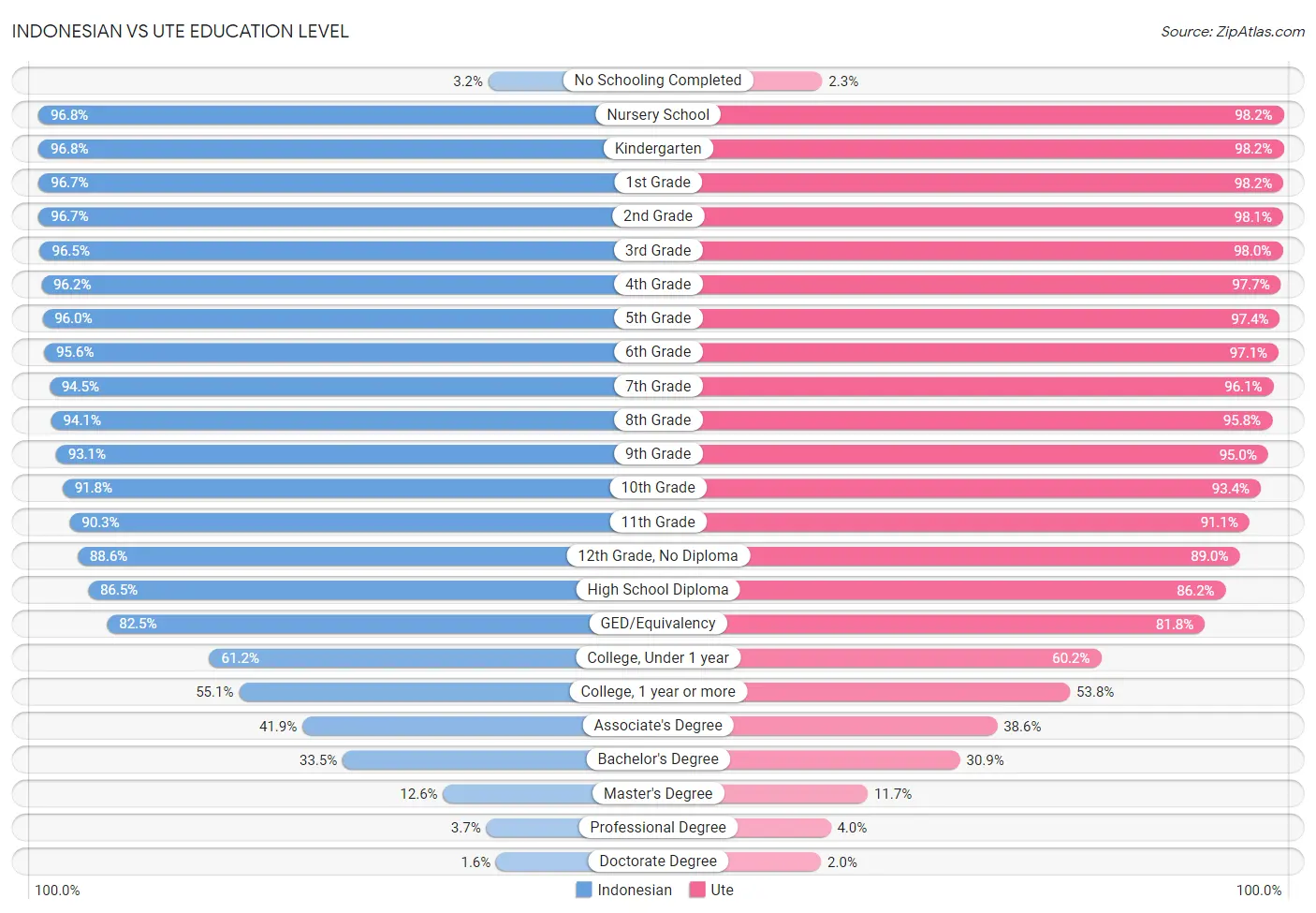
| Education Level Metric | Indonesian | Ute |
| No Schooling Completed | Tragic 3.2% | Tragic 2.3% |
| Nursery School | Tragic 96.8% | Exceptional 98.2% |
| Kindergarten | Tragic 96.8% | Exceptional 98.2% |
| 1st Grade | Tragic 96.7% | Exceptional 98.2% |
| 2nd Grade | Tragic 96.7% | Exceptional 98.1% |
| 3rd Grade | Tragic 96.5% | Exceptional 98.0% |
| 4th Grade | Tragic 96.2% | Excellent 97.7% |
| 5th Grade | Tragic 96.0% | Good 97.4% |
| 6th Grade | Tragic 95.6% | Good 97.1% |
| 7th Grade | Tragic 94.5% | Average 96.1% |
| 8th Grade | Tragic 94.1% | Average 95.8% |
| 9th Grade | Tragic 93.1% | Good 95.0% |
| 10th Grade | Tragic 91.8% | Fair 93.4% |
| 11th Grade | Tragic 90.3% | Tragic 91.1% |
| 12th Grade, No Diploma | Tragic 88.6% | Tragic 89.0% |
| High School Diploma | Tragic 86.5% | Tragic 86.2% |
| GED/Equivalency | Tragic 82.5% | Tragic 81.8% |
| College, Under 1 year | Tragic 61.2% | Tragic 60.2% |
| College, 1 year or more | Tragic 55.1% | Tragic 53.8% |
| Associate's Degree | Tragic 41.9% | Tragic 38.6% |
| Bachelor's Degree | Tragic 33.5% | Tragic 30.9% |
| Master's Degree | Tragic 12.6% | Tragic 11.7% |
| Professional Degree | Tragic 3.7% | Tragic 4.0% |
| Doctorate Degree | Tragic 1.6% | Exceptional 2.0% |
Indonesian vs Ute Disability
When considering disability, the most significant differences between Indonesian and Ute communities in the United States are seen in disability age under 5 (1.2% compared to 0.86%, a difference of 33.8%), hearing disability (3.0% compared to 3.5%, a difference of 16.8%), and disability age 65 to 74 (24.9% compared to 27.3%, a difference of 9.8%). Conversely, both communities are more comparable in terms of male disability (11.6% compared to 11.6%, a difference of 0.68%), self-care disability (2.5% compared to 2.5%, a difference of 0.77%), and disability age 35 to 64 (13.2% compared to 13.4%, a difference of 1.1%).
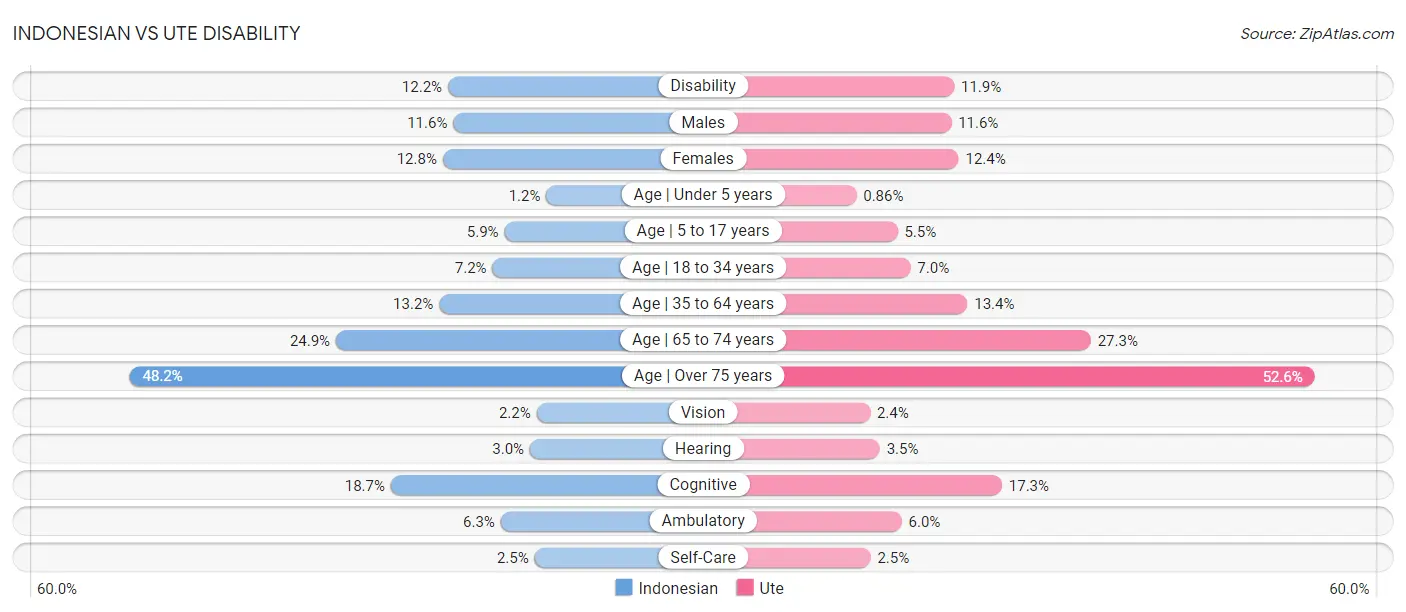
| Disability Metric | Indonesian | Ute |
| Disability | Tragic 12.2% | Poor 11.9% |
| Males | Tragic 11.6% | Tragic 11.6% |
| Females | Tragic 12.8% | Poor 12.4% |
| Age | Under 5 years | Exceptional 1.2% | Exceptional 0.86% |
| Age | 5 to 17 years | Tragic 5.9% | Excellent 5.5% |
| Age | 18 to 34 years | Tragic 7.2% | Tragic 7.0% |
| Age | 35 to 64 years | Tragic 13.2% | Tragic 13.4% |
| Age | 65 to 74 years | Tragic 24.9% | Tragic 27.3% |
| Age | Over 75 years | Tragic 48.2% | Tragic 52.6% |
| Vision | Tragic 2.2% | Tragic 2.4% |
| Hearing | Average 3.0% | Tragic 3.5% |
| Cognitive | Tragic 18.7% | Average 17.3% |
| Ambulatory | Tragic 6.3% | Excellent 6.0% |
| Self-Care | Average 2.5% | Average 2.5% |