Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar vs Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac Community Comparison
COMPARE
Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar
Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac
Social Comparison
Social Comparison
Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar
Assyrians/Chaldeans/Syriacs
3,365
SOCIAL INDEX
31.2/ 100
SOCIAL RATING
222nd/ 347
SOCIAL RANK
7,301
SOCIAL INDEX
70.5/ 100
SOCIAL RATING
124th/ 347
SOCIAL RANK
Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac Integration in Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar Communities
The statistical analysis conducted on geographies consisting of 74,102,188 people shows a moderate positive correlation between the proportion of Assyrians/Chaldeans/Syriacs within Immigrant from Burma/Myanmar communities in the United States with a correlation coefficient (R) of 0.435. On average, for every 1% (one percent) increase in Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar within a typical geography, there is an increase of 0.028% in Assyrians/Chaldeans/Syriacs. To illustrate, in a geography comprising of 100,000 individuals, a rise of 1,000 Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar corresponds to an increase of 28.0 Assyrians/Chaldeans/Syriacs.

Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar vs Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac Income
When considering income, the most significant differences between Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar and Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac communities in the United States are seen in wage/income gap (22.8% compared to 31.0%, a difference of 35.7%), householder income under 25 years ($48,749 compared to $65,329, a difference of 34.0%), and householder income ages 45 - 64 years ($91,385 compared to $110,201, a difference of 20.6%). Conversely, both communities are more comparable in terms of median female earnings ($38,028 compared to $39,159, a difference of 3.0%), median earnings ($43,998 compared to $48,304, a difference of 9.8%), and householder income over 65 years ($57,114 compared to $64,108, a difference of 12.2%).

| Income Metric | Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar | Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac |
| Per Capita Income | Tragic $39,827 | Excellent $45,195 |
| Median Family Income | Tragic $94,472 | Exceptional $109,622 |
| Median Household Income | Tragic $78,682 | Exceptional $91,991 |
| Median Earnings | Tragic $43,998 | Exceptional $48,304 |
| Median Male Earnings | Tragic $50,298 | Exceptional $58,437 |
| Median Female Earnings | Tragic $38,028 | Fair $39,159 |
| Householder Age | Under 25 years | Tragic $48,749 | Exceptional $65,329 |
| Householder Age | 25 - 44 years | Tragic $86,736 | Exceptional $101,936 |
| Householder Age | 45 - 64 years | Tragic $91,385 | Exceptional $110,201 |
| Householder Age | Over 65 years | Tragic $57,114 | Exceptional $64,108 |
| Wage/Income Gap | Exceptional 22.8% | Tragic 31.0% |
Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar vs Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac Poverty
When considering poverty, the most significant differences between Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar and Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac communities in the United States are seen in female poverty among 18-24 year olds (21.6% compared to 13.7%, a difference of 57.4%), child poverty under the age of 5 (20.4% compared to 13.6%, a difference of 50.1%), and child poverty among girls under 16 (19.7% compared to 13.3%, a difference of 47.8%). Conversely, both communities are more comparable in terms of seniors poverty over the age of 75 (12.1% compared to 10.7%, a difference of 12.7%), seniors poverty over the age of 65 (11.3% compared to 9.6%, a difference of 17.5%), and receiving food stamps (12.9% compared to 10.6%, a difference of 21.4%).
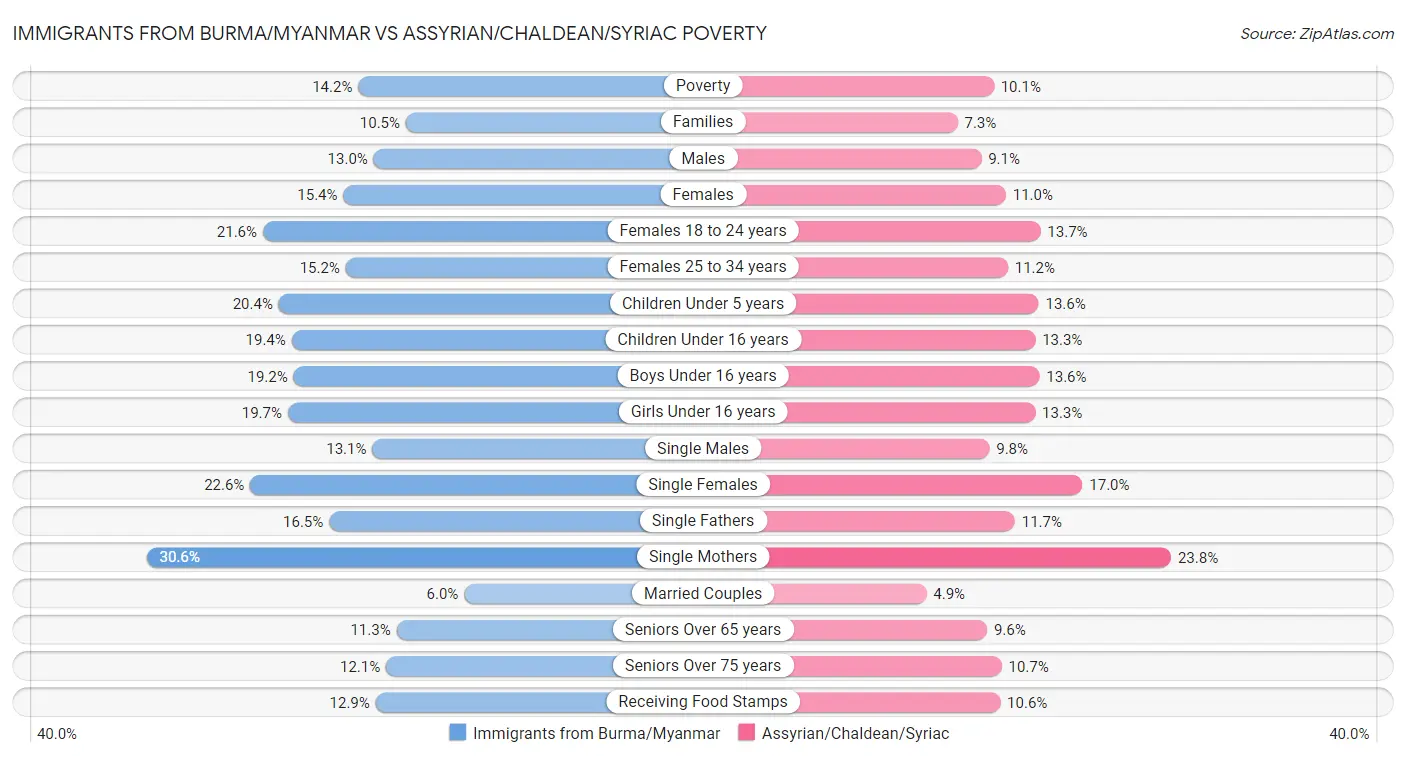
| Poverty Metric | Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar | Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac |
| Poverty | Tragic 14.2% | Exceptional 10.1% |
| Families | Tragic 10.5% | Exceptional 7.3% |
| Males | Tragic 13.0% | Exceptional 9.1% |
| Females | Tragic 15.4% | Exceptional 11.0% |
| Females 18 to 24 years | Tragic 21.6% | Exceptional 13.7% |
| Females 25 to 34 years | Tragic 15.2% | Exceptional 11.2% |
| Children Under 5 years | Tragic 20.4% | Exceptional 13.6% |
| Children Under 16 years | Tragic 19.4% | Exceptional 13.3% |
| Boys Under 16 years | Tragic 19.2% | Exceptional 13.6% |
| Girls Under 16 years | Tragic 19.7% | Exceptional 13.3% |
| Single Males | Poor 13.1% | Exceptional 9.8% |
| Single Females | Tragic 22.6% | Exceptional 17.0% |
| Single Fathers | Fair 16.5% | Exceptional 11.7% |
| Single Mothers | Tragic 30.6% | Exceptional 23.8% |
| Married Couples | Tragic 6.0% | Excellent 4.9% |
| Seniors Over 65 years | Fair 11.3% | Exceptional 9.6% |
| Seniors Over 75 years | Good 12.1% | Exceptional 10.7% |
| Receiving Food Stamps | Tragic 12.9% | Exceptional 10.6% |
Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar vs Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac Unemployment
When considering unemployment, the most significant differences between Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar and Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac communities in the United States are seen in unemployment among seniors over 75 years (7.7% compared to 11.1%, a difference of 43.1%), unemployment among ages 25 to 29 years (6.2% compared to 7.3%, a difference of 17.4%), and unemployment among ages 16 to 19 years (15.6% compared to 17.9%, a difference of 14.5%). Conversely, both communities are more comparable in terms of unemployment among ages 30 to 34 years (5.1% compared to 5.1%, a difference of 0.27%), unemployment among ages 55 to 59 years (4.4% compared to 4.5%, a difference of 1.5%), and unemployment among ages 60 to 64 years (4.4% compared to 4.5%, a difference of 2.9%).
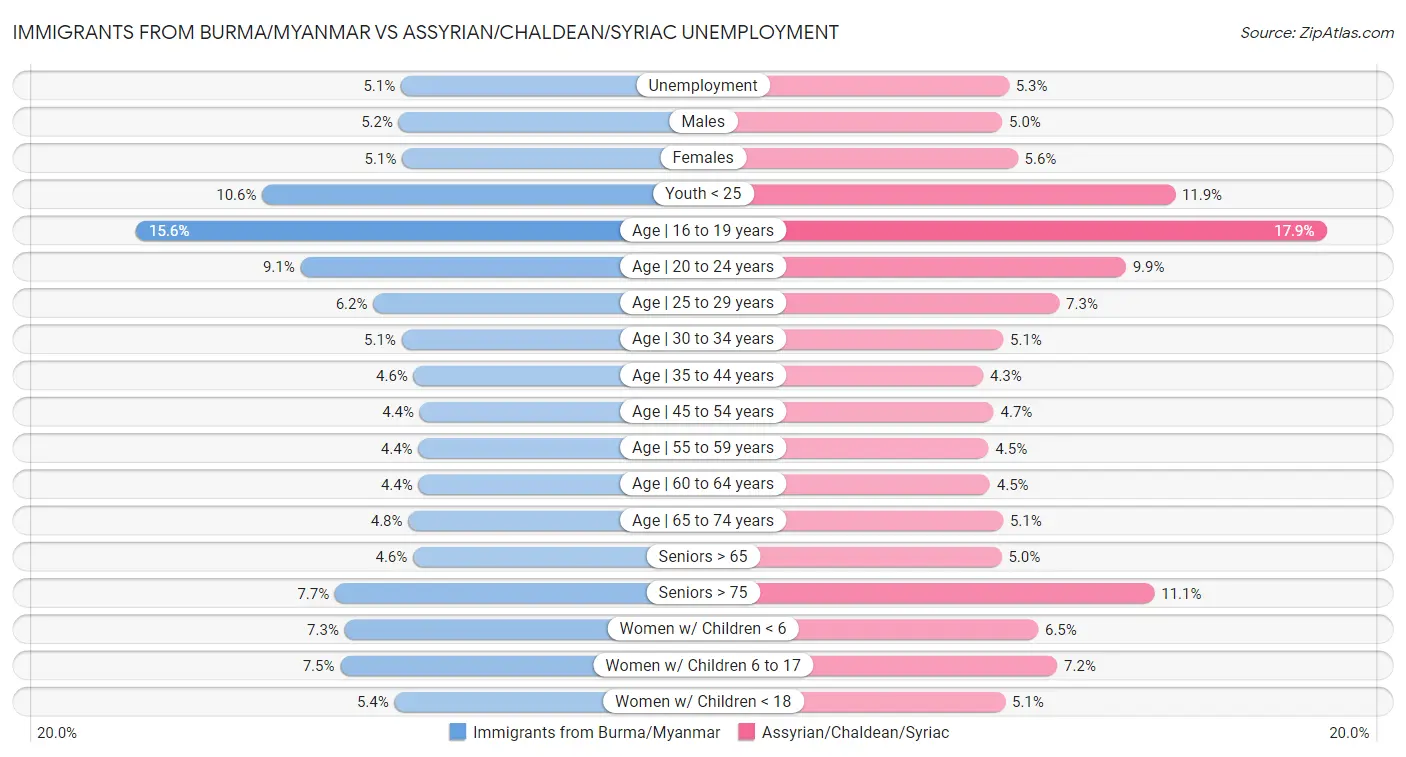
| Unemployment Metric | Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar | Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac |
| Unemployment | Excellent 5.1% | Fair 5.3% |
| Males | Good 5.2% | Exceptional 5.0% |
| Females | Exceptional 5.1% | Tragic 5.6% |
| Youth < 25 | Exceptional 10.6% | Tragic 11.9% |
| Age | 16 to 19 years | Exceptional 15.6% | Fair 17.9% |
| Age | 20 to 24 years | Exceptional 9.1% | Exceptional 9.9% |
| Age | 25 to 29 years | Exceptional 6.2% | Tragic 7.3% |
| Age | 30 to 34 years | Exceptional 5.1% | Exceptional 5.1% |
| Age | 35 to 44 years | Good 4.6% | Exceptional 4.3% |
| Age | 45 to 54 years | Exceptional 4.4% | Tragic 4.7% |
| Age | 55 to 59 years | Exceptional 4.4% | Exceptional 4.5% |
| Age | 60 to 64 years | Exceptional 4.4% | Exceptional 4.5% |
| Age | 65 to 74 years | Exceptional 4.8% | Exceptional 5.1% |
| Seniors > 65 | Exceptional 4.6% | Exceptional 5.0% |
| Seniors > 75 | Exceptional 7.7% | Tragic 11.1% |
| Women w/ Children < 6 | Exceptional 7.3% | Exceptional 6.5% |
| Women w/ Children 6 to 17 | Exceptional 7.5% | Exceptional 7.2% |
| Women w/ Children < 18 | Good 5.4% | Exceptional 5.1% |
Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar vs Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac Labor Participation
When considering labor participation, the most significant differences between Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar and Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac communities in the United States are seen in in labor force | age > 16 (66.3% compared to 64.0%, a difference of 3.5%), in labor force | age 16-19 (39.0% compared to 38.3%, a difference of 1.9%), and in labor force | age 30-34 (84.7% compared to 83.2%, a difference of 1.8%). Conversely, both communities are more comparable in terms of in labor force | age 35-44 (84.0% compared to 84.0%, a difference of 0.010%), in labor force | age 25-29 (84.7% compared to 84.7%, a difference of 0.050%), and in labor force | age 20-64 (79.7% compared to 79.4%, a difference of 0.26%).
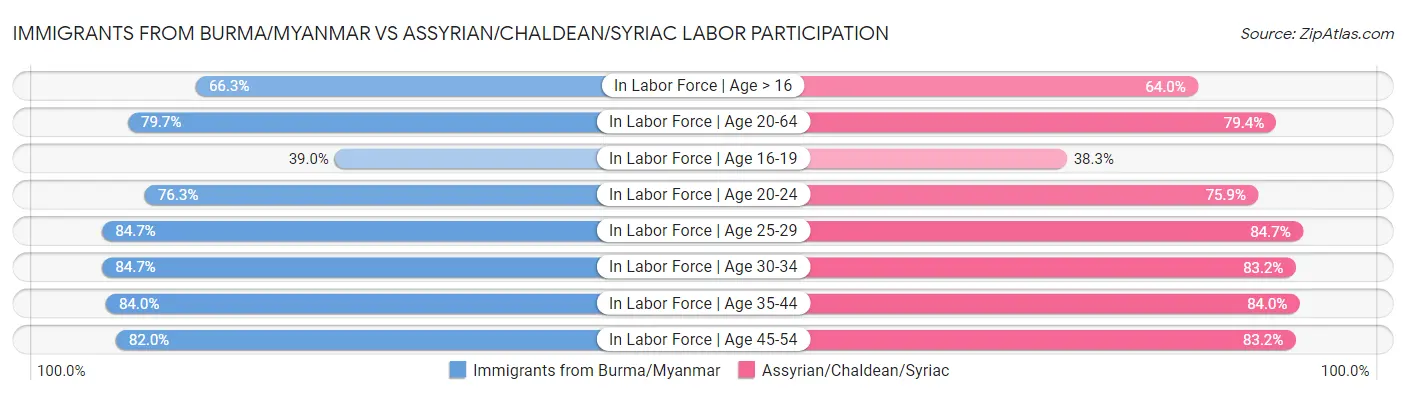
| Labor Participation Metric | Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar | Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac |
| In Labor Force | Age > 16 | Exceptional 66.3% | Tragic 64.0% |
| In Labor Force | Age 20-64 | Good 79.7% | Fair 79.4% |
| In Labor Force | Age 16-19 | Exceptional 39.0% | Exceptional 38.3% |
| In Labor Force | Age 20-24 | Exceptional 76.3% | Exceptional 75.9% |
| In Labor Force | Age 25-29 | Average 84.7% | Average 84.7% |
| In Labor Force | Age 30-34 | Average 84.7% | Tragic 83.2% |
| In Labor Force | Age 35-44 | Tragic 84.0% | Tragic 84.0% |
| In Labor Force | Age 45-54 | Tragic 82.0% | Exceptional 83.2% |
Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar vs Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac Family Structure
When considering family structure, the most significant differences between Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar and Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac communities in the United States are seen in births to unmarried women (32.9% compared to 22.0%, a difference of 49.6%), single mother households (7.0% compared to 4.8%, a difference of 46.5%), and single father households (2.4% compared to 2.0%, a difference of 23.7%). Conversely, both communities are more comparable in terms of family households with children (28.0% compared to 28.1%, a difference of 0.33%), average family size (3.29 compared to 3.24, a difference of 1.5%), and family households (62.6% compared to 68.2%, a difference of 8.9%).
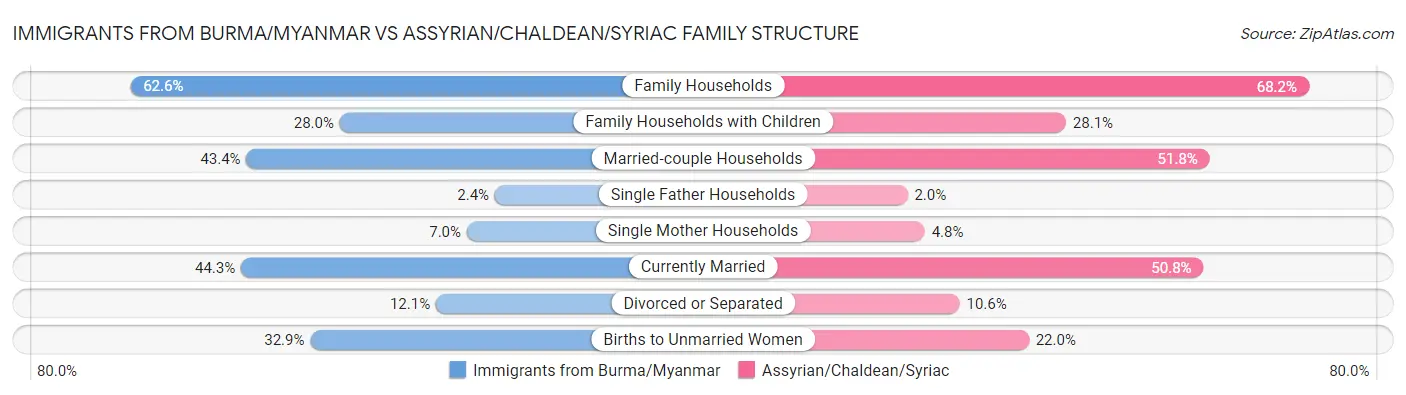
| Family Structure Metric | Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar | Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac |
| Family Households | Tragic 62.6% | Exceptional 68.2% |
| Family Households with Children | Exceptional 28.0% | Exceptional 28.1% |
| Married-couple Households | Tragic 43.4% | Exceptional 51.8% |
| Average Family Size | Exceptional 3.29 | Good 3.24 |
| Single Father Households | Poor 2.4% | Exceptional 2.0% |
| Single Mother Households | Tragic 7.0% | Exceptional 4.8% |
| Currently Married | Tragic 44.3% | Exceptional 50.8% |
| Divorced or Separated | Fair 12.1% | Exceptional 10.6% |
| Births to Unmarried Women | Poor 32.9% | Exceptional 22.0% |
Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar vs Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac Vehicle Availability
When considering vehicle availability, the most significant differences between Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar and Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac communities in the United States are seen in no vehicles in household (10.4% compared to 7.0%, a difference of 49.3%), 3 or more vehicles in household (18.8% compared to 21.7%, a difference of 15.4%), and 4 or more vehicles in household (6.2% compared to 7.2%, a difference of 14.5%). Conversely, both communities are more comparable in terms of 1 or more vehicles in household (89.7% compared to 93.0%, a difference of 3.8%), 2 or more vehicles in household (53.9% compared to 60.5%, a difference of 12.3%), and 4 or more vehicles in household (6.2% compared to 7.2%, a difference of 14.5%).
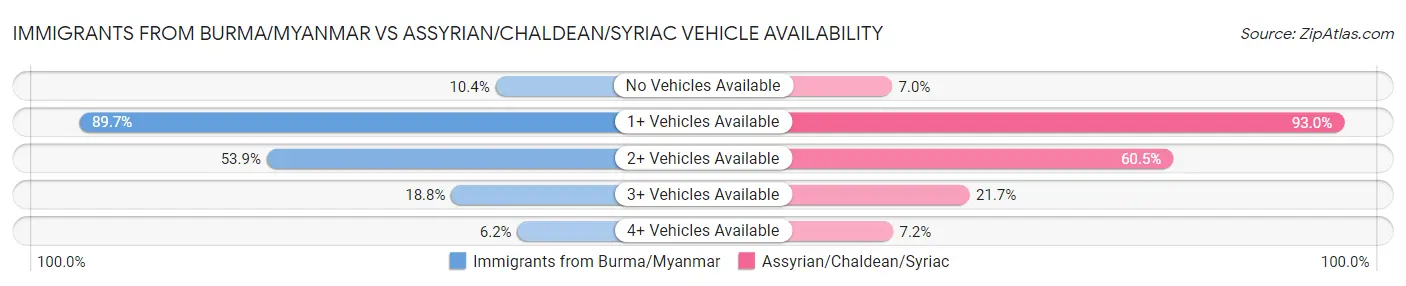
| Vehicle Availability Metric | Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar | Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac |
| No Vehicles Available | Average 10.4% | Exceptional 7.0% |
| 1+ Vehicles Available | Average 89.7% | Exceptional 93.0% |
| 2+ Vehicles Available | Tragic 53.9% | Exceptional 60.5% |
| 3+ Vehicles Available | Poor 18.8% | Exceptional 21.7% |
| 4+ Vehicles Available | Fair 6.2% | Exceptional 7.2% |
Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar vs Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac Education Level
When considering education level, the most significant differences between Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar and Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac communities in the United States are seen in no schooling completed (3.1% compared to 2.5%, a difference of 28.2%), master's degree (13.5% compared to 15.8%, a difference of 17.0%), and professional degree (3.9% compared to 4.5%, a difference of 14.5%). Conversely, both communities are more comparable in terms of nursery school (96.9% compared to 97.6%, a difference of 0.71%), kindergarten (96.8% compared to 97.5%, a difference of 0.72%), and 1st grade (96.8% compared to 97.5%, a difference of 0.73%).
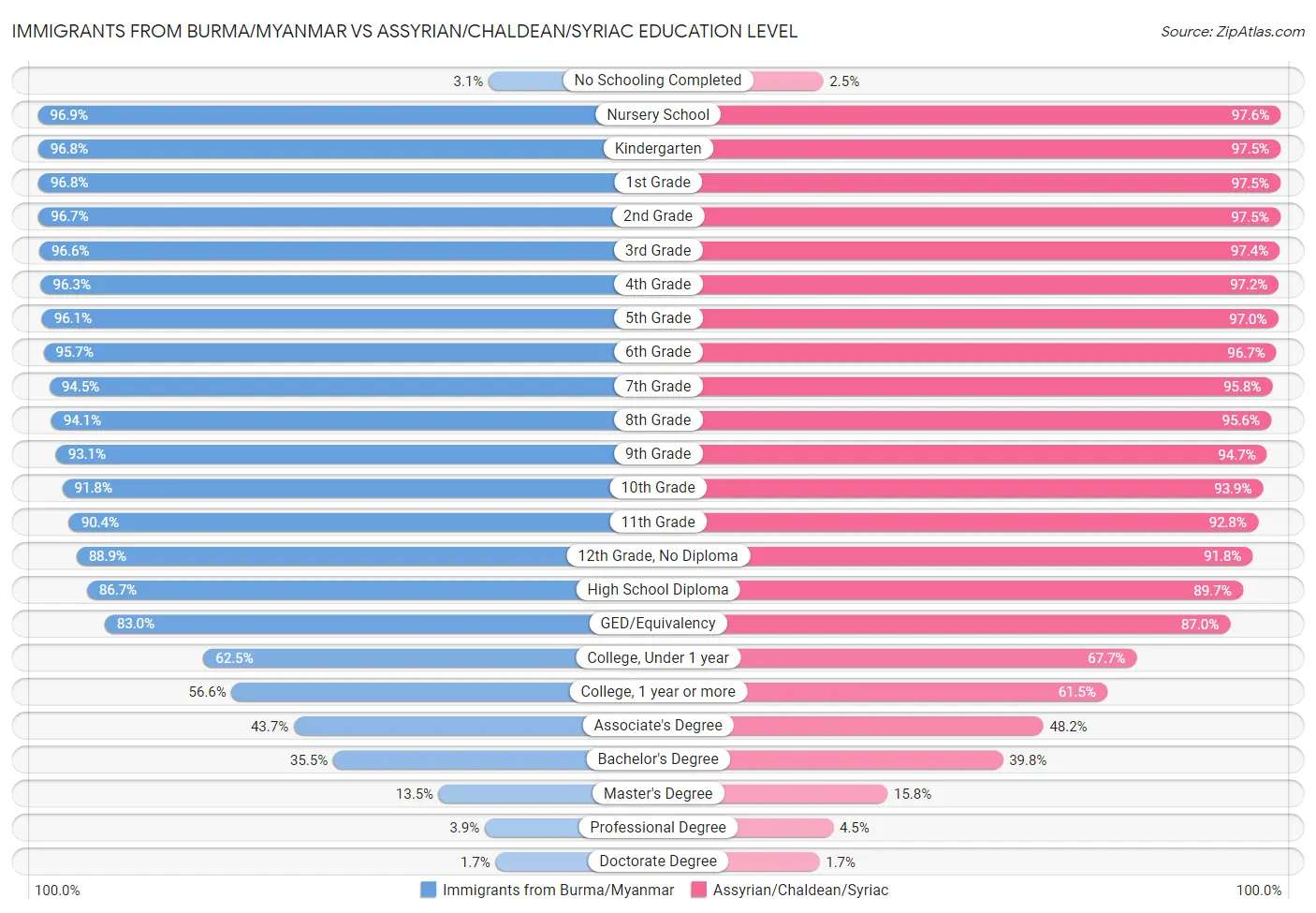
| Education Level Metric | Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar | Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac |
| No Schooling Completed | Tragic 3.1% | Tragic 2.5% |
| Nursery School | Tragic 96.9% | Tragic 97.6% |
| Kindergarten | Tragic 96.8% | Tragic 97.5% |
| 1st Grade | Tragic 96.8% | Tragic 97.5% |
| 2nd Grade | Tragic 96.7% | Tragic 97.5% |
| 3rd Grade | Tragic 96.6% | Tragic 97.4% |
| 4th Grade | Tragic 96.3% | Tragic 97.2% |
| 5th Grade | Tragic 96.1% | Tragic 97.0% |
| 6th Grade | Tragic 95.7% | Tragic 96.7% |
| 7th Grade | Tragic 94.5% | Fair 95.8% |
| 8th Grade | Tragic 94.1% | Fair 95.6% |
| 9th Grade | Tragic 93.1% | Fair 94.7% |
| 10th Grade | Tragic 91.8% | Good 93.9% |
| 11th Grade | Tragic 90.4% | Excellent 92.8% |
| 12th Grade, No Diploma | Tragic 88.9% | Excellent 91.8% |
| High School Diploma | Tragic 86.7% | Excellent 89.7% |
| GED/Equivalency | Tragic 83.0% | Exceptional 87.0% |
| College, Under 1 year | Tragic 62.5% | Exceptional 67.7% |
| College, 1 year or more | Tragic 56.6% | Exceptional 61.5% |
| Associate's Degree | Tragic 43.7% | Excellent 48.2% |
| Bachelor's Degree | Tragic 35.5% | Excellent 39.8% |
| Master's Degree | Tragic 13.5% | Excellent 15.8% |
| Professional Degree | Tragic 3.9% | Good 4.5% |
| Doctorate Degree | Poor 1.7% | Tragic 1.7% |
Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar vs Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac Disability
When considering disability, the most significant differences between Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar and Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac communities in the United States are seen in disability age 35 to 64 (12.3% compared to 10.5%, a difference of 16.9%), self-care disability (2.5% compared to 2.8%, a difference of 15.6%), and hearing disability (2.9% compared to 3.3%, a difference of 13.2%). Conversely, both communities are more comparable in terms of female disability (12.4% compared to 12.5%, a difference of 0.53%), disability (11.8% compared to 11.9%, a difference of 1.1%), and male disability (11.2% compared to 11.4%, a difference of 1.7%).
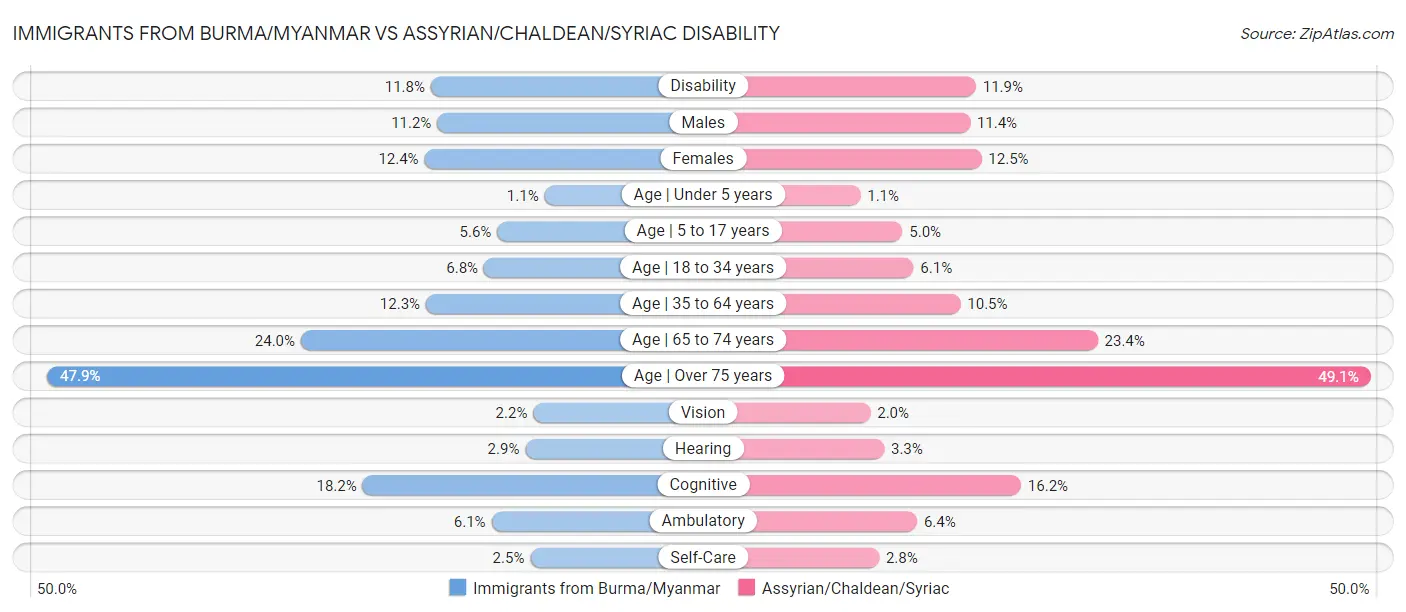
| Disability Metric | Immigrants from Burma/Myanmar | Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac |
| Disability | Fair 11.8% | Poor 11.9% |
| Males | Average 11.2% | Fair 11.4% |
| Females | Poor 12.4% | Tragic 12.5% |
| Age | Under 5 years | Exceptional 1.1% | Exceptional 1.1% |
| Age | 5 to 17 years | Average 5.6% | Exceptional 5.0% |
| Age | 18 to 34 years | Poor 6.8% | Exceptional 6.1% |
| Age | 35 to 64 years | Tragic 12.3% | Exceptional 10.5% |
| Age | 65 to 74 years | Poor 24.0% | Average 23.4% |
| Age | Over 75 years | Poor 47.9% | Tragic 49.1% |
| Vision | Fair 2.2% | Exceptional 2.0% |
| Hearing | Good 2.9% | Tragic 3.3% |
| Cognitive | Tragic 18.2% | Exceptional 16.2% |
| Ambulatory | Average 6.1% | Tragic 6.4% |
| Self-Care | Average 2.5% | Tragic 2.8% |