Czech vs Immigrants from Singapore Family Poverty
COMPARE
Czech
Immigrants from Singapore
Family Poverty
Family Poverty Comparison
Czechs
Immigrants from Singapore
7.4%
FAMILY POVERTY
99.6/ 100
METRIC RATING
31st/ 347
METRIC RANK
7.1%
FAMILY POVERTY
99.8/ 100
METRIC RATING
11th/ 347
METRIC RANK
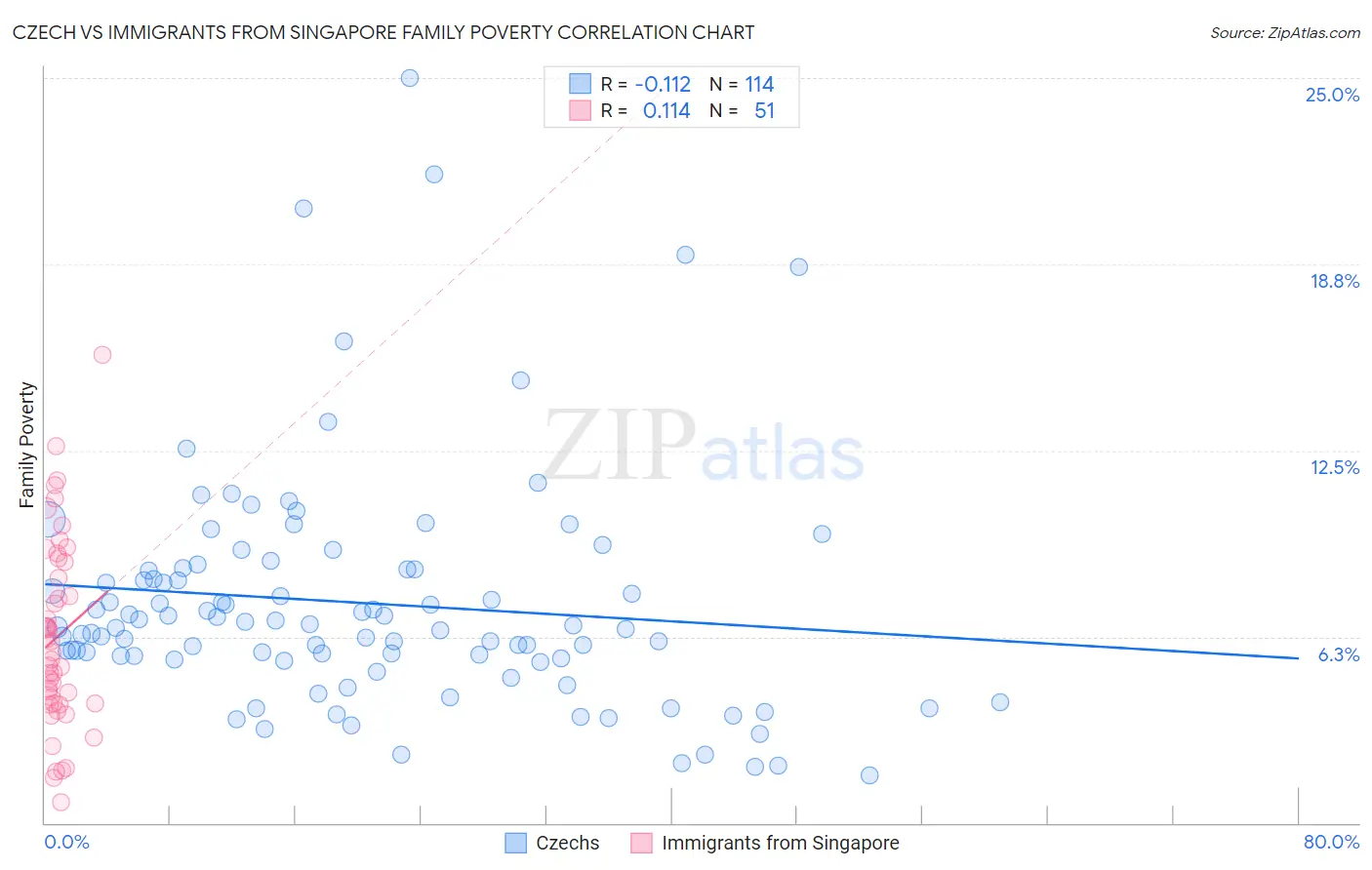
Czech vs Immigrants from Singapore Family Poverty Correlation Chart
The statistical analysis conducted on geographies consisting of 482,390,324 people shows a poor negative correlation between the proportion of Czechs and poverty level among families in the United States with a correlation coefficient (R) of -0.112 and weighted average of 7.4%. Similarly, the statistical analysis conducted on geographies consisting of 137,322,674 people shows a poor positive correlation between the proportion of Immigrants from Singapore and poverty level among families in the United States with a correlation coefficient (R) of 0.114 and weighted average of 7.1%, a difference of 4.5%.
Family Poverty Correlation Summary
| Measurement | Czech | Immigrants from Singapore |
| Minimum | 1.6% | 0.70% |
| Maximum | 25.0% | 15.7% |
| Range | 23.4% | 15.0% |
| Mean | 7.4% | 6.2% |
| Median | 6.6% | 5.7% |
| Interquartile 25% (IQ1) | 5.5% | 4.0% |
| Interquartile 75% (IQ3) | 8.5% | 8.8% |
| Interquartile Range (IQR) | 3.0% | 4.8% |
| Standard Deviation (Sample) | 4.0% | 3.2% |
| Standard Deviation (Population) | 3.9% | 3.1% |
Demographics Similar to Czechs and Immigrants from Singapore by Family Poverty
In terms of family poverty, the demographic groups most similar to Czechs are Italian (7.4%, a difference of 0.12%), Immigrants from Northern Europe (7.4%, a difference of 0.41%), Immigrants from Korea (7.4%, a difference of 0.58%), Immigrants from Scotland (7.3%, a difference of 0.97%), and Cypriot (7.3%, a difference of 0.99%). Similarly, the demographic groups most similar to Immigrants from Singapore are Maltese (7.1%, a difference of 0.29%), Swedish (7.1%, a difference of 0.34%), Iranian (7.1%, a difference of 0.34%), Lithuanian (7.2%, a difference of 1.2%), and Immigrants from South Central Asia (7.2%, a difference of 1.5%).
| Demographics | Rating | Rank | Family Poverty |
| Immigrants | Singapore | 99.8 /100 | #11 | Exceptional 7.1% |
| Maltese | 99.8 /100 | #12 | Exceptional 7.1% |
| Swedes | 99.8 /100 | #13 | Exceptional 7.1% |
| Iranians | 99.8 /100 | #14 | Exceptional 7.1% |
| Lithuanians | 99.8 /100 | #15 | Exceptional 7.2% |
| Immigrants | South Central Asia | 99.8 /100 | #16 | Exceptional 7.2% |
| Luxembourgers | 99.8 /100 | #17 | Exceptional 7.2% |
| Immigrants | Lithuania | 99.8 /100 | #18 | Exceptional 7.2% |
| Eastern Europeans | 99.7 /100 | #19 | Exceptional 7.2% |
| Immigrants | Hong Kong | 99.7 /100 | #20 | Exceptional 7.3% |
| Immigrants | Iran | 99.7 /100 | #21 | Exceptional 7.3% |
| Danes | 99.7 /100 | #22 | Exceptional 7.3% |
| Assyrians/Chaldeans/Syriacs | 99.7 /100 | #23 | Exceptional 7.3% |
| Croatians | 99.7 /100 | #24 | Exceptional 7.3% |
| Burmese | 99.7 /100 | #25 | Exceptional 7.3% |
| Cypriots | 99.6 /100 | #26 | Exceptional 7.3% |
| Immigrants | Scotland | 99.6 /100 | #27 | Exceptional 7.3% |
| Immigrants | Korea | 99.6 /100 | #28 | Exceptional 7.4% |
| Immigrants | Northern Europe | 99.6 /100 | #29 | Exceptional 7.4% |
| Italians | 99.6 /100 | #30 | Exceptional 7.4% |
| Czechs | 99.6 /100 | #31 | Exceptional 7.4% |