Immigrants from Northern Europe vs Iranian Family Poverty
COMPARE
Immigrants from Northern Europe
Iranian
Family Poverty
Family Poverty Comparison
Immigrants from Northern Europe
Iranians
7.4%
FAMILY POVERTY
99.6/ 100
METRIC RATING
29th/ 347
METRIC RANK
7.1%
FAMILY POVERTY
99.8/ 100
METRIC RATING
14th/ 347
METRIC RANK
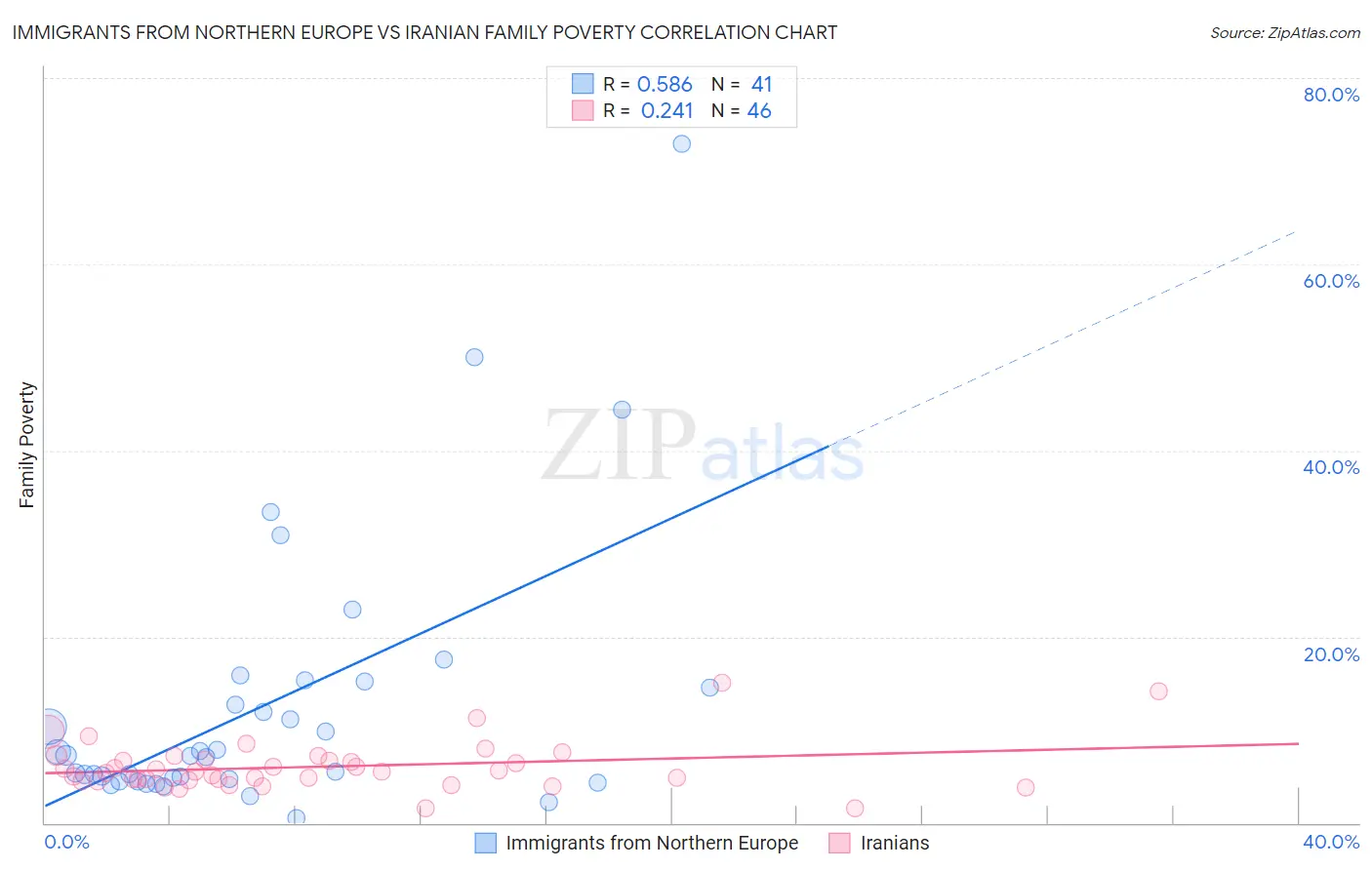
Immigrants from Northern Europe vs Iranian Family Poverty Correlation Chart
The statistical analysis conducted on geographies consisting of 475,098,586 people shows a substantial positive correlation between the proportion of Immigrants from Northern Europe and poverty level among families in the United States with a correlation coefficient (R) of 0.586 and weighted average of 7.4%. Similarly, the statistical analysis conducted on geographies consisting of 316,120,313 people shows a weak positive correlation between the proportion of Iranians and poverty level among families in the United States with a correlation coefficient (R) of 0.241 and weighted average of 7.1%, a difference of 3.7%.
Family Poverty Correlation Summary
| Measurement | Immigrants from Northern Europe | Iranian |
| Minimum | 0.50% | 1.6% |
| Maximum | 72.9% | 15.0% |
| Range | 72.4% | 13.4% |
| Mean | 12.6% | 6.0% |
| Median | 7.3% | 5.5% |
| Interquartile 25% (IQ1) | 4.6% | 4.5% |
| Interquartile 75% (IQ3) | 14.9% | 6.8% |
| Interquartile Range (IQR) | 10.3% | 2.3% |
| Standard Deviation (Sample) | 14.6% | 2.6% |
| Standard Deviation (Population) | 14.4% | 2.6% |
Demographics Similar to Immigrants from Northern Europe and Iranians by Family Poverty
In terms of family poverty, the demographic groups most similar to Immigrants from Northern Europe are Immigrants from Korea (7.4%, a difference of 0.17%), Italian (7.4%, a difference of 0.29%), Czech (7.4%, a difference of 0.41%), Immigrants from Scotland (7.3%, a difference of 0.55%), and Cypriot (7.3%, a difference of 0.57%). Similarly, the demographic groups most similar to Iranians are Swedish (7.1%, a difference of 0.010%), Maltese (7.1%, a difference of 0.060%), Immigrants from Singapore (7.1%, a difference of 0.34%), Lithuanian (7.2%, a difference of 0.88%), and Immigrants from South Central Asia (7.2%, a difference of 1.1%).
| Demographics | Rating | Rank | Family Poverty |
| Immigrants | Singapore | 99.8 /100 | #11 | Exceptional 7.1% |
| Maltese | 99.8 /100 | #12 | Exceptional 7.1% |
| Swedes | 99.8 /100 | #13 | Exceptional 7.1% |
| Iranians | 99.8 /100 | #14 | Exceptional 7.1% |
| Lithuanians | 99.8 /100 | #15 | Exceptional 7.2% |
| Immigrants | South Central Asia | 99.8 /100 | #16 | Exceptional 7.2% |
| Luxembourgers | 99.8 /100 | #17 | Exceptional 7.2% |
| Immigrants | Lithuania | 99.8 /100 | #18 | Exceptional 7.2% |
| Eastern Europeans | 99.7 /100 | #19 | Exceptional 7.2% |
| Immigrants | Hong Kong | 99.7 /100 | #20 | Exceptional 7.3% |
| Immigrants | Iran | 99.7 /100 | #21 | Exceptional 7.3% |
| Danes | 99.7 /100 | #22 | Exceptional 7.3% |
| Assyrians/Chaldeans/Syriacs | 99.7 /100 | #23 | Exceptional 7.3% |
| Croatians | 99.7 /100 | #24 | Exceptional 7.3% |
| Burmese | 99.7 /100 | #25 | Exceptional 7.3% |
| Cypriots | 99.6 /100 | #26 | Exceptional 7.3% |
| Immigrants | Scotland | 99.6 /100 | #27 | Exceptional 7.3% |
| Immigrants | Korea | 99.6 /100 | #28 | Exceptional 7.4% |
| Immigrants | Northern Europe | 99.6 /100 | #29 | Exceptional 7.4% |
| Italians | 99.6 /100 | #30 | Exceptional 7.4% |
| Czechs | 99.6 /100 | #31 | Exceptional 7.4% |